Polyphosphazenes as Adjuvants for Animal Vaccines and Other Medical Applications
- PMID: 33763409
- PMCID: PMC7982900
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.625482
Polyphosphazenes as Adjuvants for Animal Vaccines and Other Medical Applications
Abstract
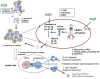
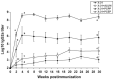
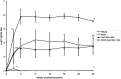
Polyphosphazenes are a class of experimental adjuvants that have shown great versatility as vaccine adjuvants in many animal species ranging from laboratory rodents to large animal species. Their adjuvant activity has shown promising results with numerous viral and bacterial antigens, as well as with crude and purified antigens. Vaccines adjuvanted with polyphosphazenes can be delivered via systemic and mucosal administration including respiratory, oral, rectal, and intravaginal routes. Polyphosphazenes can be used in combination with other adjuvants, further enhancing immune responses to antigens. The mechanisms of action of polyphosphazenes have not fully been defined, but several systematic studies have suggested that they act primarily by activating innate immunity. In the present review, we will highlight progress in the development of polyphosphazenes as adjuvants in animals and their other medical applications.
Keywords: adjuvants; animals; bacteria; immunity; polyphosphazenes; vaccines; viruses.
Copyright © 2021 Chand, Magiri, Wilson and Mutwiri.
Conflict of interest statement
GM holds a patent in polyphosphazene adjuvants and their combinations. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The potential of polyphosphazenes for delivery of vaccine antigens and immunotherapeutic agents.Curr Drug Deliv. 2010 Jan;7(1):13-20. doi: 10.2174/156720110790396481. Curr Drug Deliv. 2010. PMID: 19863483 Review.
-
Co-administration of polyphosphazenes with CpG oligodeoxynucleotides strongly enhances immune responses in mice immunized with Hepatitis B virus surface antigen.Vaccine. 2008 May 23;26(22):2680-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.03.031. Epub 2008 Apr 3. Vaccine. 2008. PMID: 18430493
-
Recent advances in experimental polyphosphazene adjuvants and their mechanisms of action.Cell Tissue Res. 2018 Dec;374(3):465-471. doi: 10.1007/s00441-018-2929-4. Epub 2018 Oct 8. Cell Tissue Res. 2018. PMID: 30294754 Review.
-
Modes of Action for Mucosal Vaccine Adjuvants.Viral Immunol. 2017 Jul/Aug;30(6):463-470. doi: 10.1089/vim.2017.0026. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Viral Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28436755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intranasal vaccination with an adjuvanted polyphosphazenes nanoparticle-based vaccine formulation stimulates protective immune responses in mice.Nanomedicine. 2017 Oct;13(7):2169-2178. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2017.05.012. Epub 2017 Jun 1. Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28579436
Cited by
-
Polyphosphazene-Based Biomaterials for Biomedical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 15;23(24):15993. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415993. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virus-Mimicking Polymer Nanocomplexes Co-Assembling HCV E1E2 and Core Proteins with TLR 7/8 Agonist-Synthesis, Characterization, and In Vivo Activity.J Funct Biomater. 2025 Jan 19;16(1):34. doi: 10.3390/jfb16010034. J Funct Biomater. 2025. PMID: 39852590 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphazene Cyclomatrix Network-Based Polymer: Chemistry, Synthesis, and Applications.ACS Omega. 2022 Aug 9;7(33):28694-28707. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01573. eCollection 2022 Aug 23. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36033672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryo-EM and AFM visualize linear polyorganophosphazene: individual chains and single-chain assemblies with proteins.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 31:rs.3.rs-3411603. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3411603/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Commun Mater. 2024;5:36. doi: 10.1038/s43246-024-00476-6. PMID: 37961436 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Nanodispersions of Polyelectrolytes Based on Humic Substances: Isolation, Physico-Chemical Characterization and Evaluation of Biological Activity.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Nov 18;13(11):1954. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13111954. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34834368 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

