Membrane Remodeling by Arc/Arg3.1
- PMID: 33763452
- PMCID: PMC7982473
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.630625
Membrane Remodeling by Arc/Arg3.1
Abstract
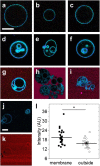
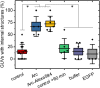
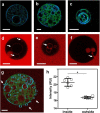
The activity-regulated cytoskeletal-associated protein (Arc, also known as Arg3.1) is an immediate early gene product induced by activity/experience and required for multiple modes of synaptic plasticity. Both long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) are impaired upon Arc deletion, as well as the ability to form long-term spatial, taste and fear memories. The best-characterized cellular function of Arc is enhancement of the endocytic internalization of AMPA receptors (AMPARs) in dendritic spines. Solution of the crystal structure of a C-terminal segment of Arc revealed a striking similarity to the capsid domain of HIV Gag. It was subsequently shown that Arc assembles into viral capsid-like structures that enclose Arc mRNA, are released into the extracellular space, and are internalized by neighboring cells. Thus, Arc is unique in participating in plasma membrane budding both into and out of the cell. In this report we study the interaction of Arc with membranes using giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs). Using the fluorescent lipid probe LAURDAN, we find that Arc promotes the formation of smaller vesicles that penetrate into the GUV interior. Our results suggest that Arc induces negative membrane curvature and may therefore facilitate the formation of mRNA-containing extracellular vesicles from the plasma membrane.
Keywords: Arc; GUV; fluorescence; giant unilamellar vesicle; membrane budding; membrane remodeling.
Copyright © 2021 Hedde, Malacrida, Barylko, Binns, Albanesi and Jameson.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Angelova M. I., Dimitrov D. S. (1986). Liposome electroformation. Faraday Discuss. Chem. Soc. 81, 303–311. 10.1039/DC9868100303 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

