Multiparametric vs. Inferior Vena Cava-Based Estimation of Right Atrial Pressure
- PMID: 33763459
- PMCID: PMC7982413
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.632302
Multiparametric vs. Inferior Vena Cava-Based Estimation of Right Atrial Pressure
Abstract
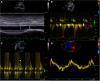
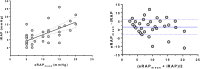
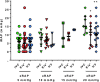
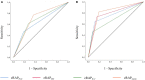
Background: Right atrial pressure (RAP) can be estimated by echocardiography from inferior vena cava diameter and collapsibility (eRAPIVC), tricuspid E/e' ratio ( ), or hepatic vein flow (eRAPHV). The mean of these estimates (eRAPmean) might be more accurate than single assessments. Methods and Results: eRAPIVC, , eRAPHV (categorized in 5, 10, 15, or 20 mmHg), eRAPmean (continuous values) and invasive RAP (iRAP) were obtained in 43 consecutive patients undergoing right heart catheterization [median age 69 (58-75) years, 49% males]. There was a positive correlation between eRAPmean and iRAP (Spearman test r = 0.66, P < 0.001), with Bland-Altman test showing the best agreement for values <10 mmHg. There was also a trend for decreased concordance between eRAPIVC, , eRAPHV, and iRAP across the 5- to 20-mmHg categories, and iRAP was significantly different from and eRAPHV for the 20-mmHg category (Wilcoxon signed-rank test P = 0.02 and P < 0.001, respectively). The areas under the curve in predicting iRAP were nonsignificantly better for eRAPmean than for eRAPIVC at both 5-mmHg [0.64, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.49-0.80 vs. 0.70, 95% CI 0.53-0.87; Wald test P = 0.41] and 10-mmHg (0.76, 95% CI 0.60-0.92 vs. 0.81, 95% CI 0.67-0.96; P = 0.43) thresholds. Conclusions: Our data suggest that multiparametric eRAPmean does not provide advantage over eRAPIVC, despite being more complex and time-consuming.
Keywords: echocardiograghy; heart failure; pulmonary hypertension; right atrial pressure; right heart catheterization.
Copyright © 2021 Toma, Giovinazzo, Crimi, Masoero, Balbi, Montecucco, Canepa, Porto and Ameri.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J. 2016 37:67–119. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv317 - DOI - PubMed
-
- van den Bosch AE, Badano LP, Grapsa J. Right ventricle and pulmonary arterial pressure. In: The EACVI Textbook of Echocardiography. Oxford University Press: (2017). p. 171–84.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

