Machine learning-based decision tree classifier for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration
- PMID: 33763863
- PMCID: PMC9292481
- DOI: 10.1111/nan.12710
Machine learning-based decision tree classifier for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration
Abstract
Aims: This study aimed to clarify the different topographical distribution of tau pathology between progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) and corticobasal degeneration (CBD) and establish a machine learning-based decision tree classifier.
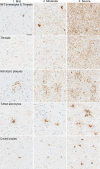
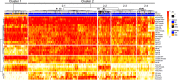
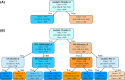
Methods: Paraffin-embedded sections of the temporal cortex, motor cortex, caudate nucleus, globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, substantia nigra, red nucleus, and midbrain tectum from 1020 PSP and 199 CBD cases were assessed by phospho-tau immunohistochemistry. The severity of tau lesions (i.e., neurofibrillary tangle, coiled body, tufted astrocyte or astrocytic plaque, and tau threads) was semi-quantitatively scored in each region. Hierarchical cluster analysis was performed using tau pathology scores. A decision tree classifier was made with tau pathology scores using 914 cases. Cross-validation was done using 305 cases. An additional ten cases were used for a validation study.
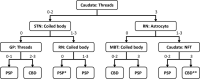
Results: Cluster analysis displayed two distinct clusters; the first cluster included only CBD, and the other cluster included all PSP and six CBD cases. We built a decision tree, which used only seven decision nodes. The scores of tau threads in the caudate nucleus were the most decisive factor for predicting CBD. In a cross-validation, 302 out of 305 cases were correctly diagnosed. In the pilot validation study, three investigators made a correct diagnosis in all cases using the decision tree.
Conclusion: Regardless of the morphology of astrocytic tau lesions, semi-quantitative tau pathology scores in select brain regions are sufficient to distinguish PSP and CBD. The decision tree simplifies neuropathologic differential diagnosis of PSP and CBD.
Keywords: Machine learning; corticobasal degeneration; corticobasal syndrome; decision tree classifier; hierarchical cluster analysis; progressive supranuclear palsy.
© 2021 The Authors. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Neuropathological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Steele JC, Richardson JC, Olszewski J. Progressive supranuclear palsy. A heterogeneous degeneration involving the brain stem, basal ganglia and cerebellum with vertical gaze and pseudobulbar palsy, nuchal dystonia and dementia. Arch Neurol. 1964;10:333‐359. - PubMed
-
- Dickson DW, Bergeron C, Chin SS, et al. Office of rare diseases neuropathologic criteria for corticobasal degeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2002;61:935‐946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

