Serum insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 levels as biomarker for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma-associated malnutrition and muscle wasting
- PMID: 33763996
- PMCID: PMC8200427
- DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.12692
Serum insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 levels as biomarker for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma-associated malnutrition and muscle wasting
Abstract
Background: Malnutrition and muscle wasting are common features frequently observed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) patients with cancer cachexia. They are associated with reduced survival and quality of life. Nutrition therapy is an important part of multimodal cancer care in PDAC. However, due to the complexity of nutrition assessment, only 30-60% of patients with nutritional risks receive nutritional treatment at present. It is important to identify biomarkers that may be used to improve management of PDAC-associated malnutrition. Serum insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 (IGFBP2) has emerged as a potential serum biomarker in a variety of tumours. However, its association with malnutrition and muscle wasting in PDAC is unclear.
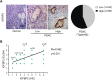
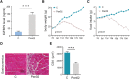
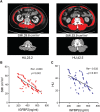
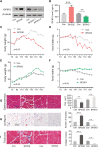
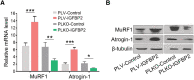
Methods: We evaluated the tumour IGFBP2 expression and serum IGFBP2 level in 98 PDAC patients using immunohistochemistry and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and analysed the correlation between them. Furthermore, we explored the relationship between IGFBP2 of both tumour and serum and nutritional status (Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment and skeletal muscle index). Pan02 IGFBP2 stable transfection cell lines, Pan02 PLV-IGFBP2 cells, and PLKO-IGFBP2 cells were injected subcutaneously into the flank of C57BL/6 mouse. Serum IGFBP2 levels, food intake, and body weight of these mice were measured. The degree of muscle atrophy is characterized by haematoxylin and eosin, Oil Red O, and Masson's trichrome staining. The mRNA and protein expression of several essential muscle-related signal proteins such as atrogin-1 and muscle RING finger 1 was measured.
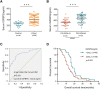
Results: Among 98 patients, we found that tumour IGFBP2 expression is related to plasma IGFBP2 levels (rs = 0.562, P < 0.001), and they significantly increased among patients with Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment ≥9 and correlated with overall survival. Moreover, serum IGFBP2 level is negatively correlated with skeletal muscle index (rs = -0.600, P < 0.001) and Hounsfield units (rs = -0.532, P < 0.001). In mice injected with Pan02 PLV-IGFBP2 cell, circulating IGFBP2 was elevated while body weight and food intake were decreased when compared with Pan02 PLV-Control group. These mice also exhibited significantly aggravated muscle fibre atrophy, lipid deposition, and increased collagen tissue, and the expression of mRNA and protein of atrogin-1 and muscle RING finger 1 in the gastrocnemius muscle is increased. Conversely, these symptoms were alleviated in the PLKO-IGFBP2 group.
Conclusions: In the current study, there is a significant correlation between serum IGFBP2 levels, malnutrition, and muscle atrophy in PDAC. Our results suggested that serum IGFBP2 level might be a promising biomarker and intervention targets for PDAC-associated severe malnutrition and muscle wasting.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cachexia; IGFBP2; Malnutrition; Muscle wasting; PDAC.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society on Sarcopenia, Cachexia and Wasting Disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The systemic activin response to pancreatic cancer: implications for effective cancer cachexia therapy.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2019 Oct;10(5):1083-1101. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12461. Epub 2019 Jul 8. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2019. PMID: 31286691 Free PMC article.
-
Sex specificity of pancreatic cancer cachexia phenotypes, mechanisms, and treatment in mice and humans: role of Activin.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022 Aug;13(4):2146-2161. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12998. Epub 2022 May 5. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022. PMID: 35510530 Free PMC article.
-
Increased myocellular lipid and IGFBP-3 expression in a pre-clinical model of pancreatic cancer-related skeletal muscle wasting.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021 Jun;12(3):731-745. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12699. Epub 2021 May 7. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021. PMID: 33960737 Free PMC article.
-
Role of noncoding RNAs in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma associated cachexia.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 Dec 1;323(6):C1624-C1632. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00424.2022. Epub 2022 Oct 24. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36280389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Muscle wasting in cancer.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Oct;45(10):2215-29. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.05.032. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23770121 Review.
Cited by
-
A tumor-secreted protein utilizes glucagon release to cause host wasting.Cell Discov. 2025 Feb 10;11(1):11. doi: 10.1038/s41421-024-00762-0. Cell Discov. 2025. PMID: 39924534 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Waist Circumference and Circulating Levels of IGFBP-2 as a Simple Screening Tool for Early Detection of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Sep 5;17:3335-3341. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S466051. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 39252871 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Cytokine-Induced Hepatic Gluconeogenesis Contributes to Cancer Cachexia: Insights from Full Body Single Nuclei Sequencing.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 18:2023.05.15.540823. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.15.540823. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37292804 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Serum insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 as a potential biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Ann Med. 2022 Dec;54(1):2153-2166. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2104921. Ann Med. 2022. PMID: 35930383 Free PMC article.
-
CA 19-9 but Not IGF-1/IGFBP-2 Is a Useful Biomarker for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and Chronic Pancreatitis (CP) Differentiation.J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 14;12(12):4050. doi: 10.3390/jcm12124050. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37373743 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Inui A. Cancer anorexia‐cachexia syndrome: current issues in research and management. CA Cancer J Clin 2002;52:72–91. - PubMed
-
- Biswas AK, Acharyya S. Understanding cachexia in the context of metastatic progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2020;20:274–284. - PubMed
-
- Madeddu C, Mantovani G, Gramignano G, Astara G, Macciò A. Muscle wasting as main evidence of energy impairment in cancer cachexia: future therapeutic approaches. Future Oncol 2015;11:2697–2710. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt SF, Rohm M, Herzig S, Diaz MB. Cancer cachexia: more than skeletal muscle wasting. Trends Cancer 2018;4:849–860. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

