Subclinical left ventricular dysfunction in men under androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer, revealed by speckle-tracking-derived parameters, repolarization, and myocardial injury markers
- PMID: 33764596
- PMCID: PMC8252497
- DOI: 10.1111/echo.15043
Subclinical left ventricular dysfunction in men under androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer, revealed by speckle-tracking-derived parameters, repolarization, and myocardial injury markers
Abstract
Objective: To analyze global left ventricular longitudinal strain (GLS), mechanical dispersion (MD), electrocardiographic repolarization, and myocardial injury markers changes during androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) and subsequent hypogonadism in men with advanced prostate cancer.
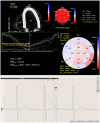
Methods: We included 31 patients 69.7 ± 7.3 years old, in sinus rhythm, with stable cardiac conditions and evaluated them by echocardiography, electrocardiography, and blood sampling for high sensitivity cardiac troponin I (hs-cTnI), and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NTproBNP), at ADT initiation (M0) and after 6 months of treatment (M1). Peak longitudinal strain by speckle-tracking echocardiography was assessed in 17 left ventricular segments and averaged to GLS. Standard deviation of time intervals from the start of Q/R on electrocardiogram to peak longitudinal strain in the 17 segments (MDSD ), and the difference between the longest and shortest time-to-peak strain intervals (MDdelta ) were calculated as indices of MD. Fridericia corrected electrocardiographic repolarization parameters were analyzed as follows: QT interval (QTc), mean and maximum values of Tpeak-Tend interval (Tpe), and Tpe/QT ratio, Tpe dispersion (Tped).
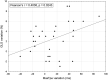
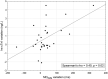
Results: Significant impairments of the following parameters were registered between M0 and M1: GLS (%) (-16.93 ± 3.89; -14.43 ± 3.57, P < .001), MDSD (ms) (77.4 ± 21.4; 89 ± 27, P = .004), MDdelta (ms) (225.3 ± 78.3; 259.9 ± 108.4, P = .02), QTc (ms) (458.8 ± 43.4; 485.6 ± 45.1, P = .01), maxTpe/QT (0.246 ± 0.04; 0.268 ± 0.04, P = .01), maxTpe (ms) (105.4 ± 23.2; 119.5 ± 26.4 P = .01), meanTpe (ms) (83.3 ± 16.8; 90.7 ± 19.3, P = .02), and hs-cTnI (ng/mL) (4.6 ± 5.4; 5.4 ± 6.4, P = .01). Mean serum testosterone level at M1 was 0.1 ± 0.13 ng/mL. The patients' clinical cardiological status remained stable during follow-up.
Conclusions: ADT and subsequent hypogonadism induce subclinical alterations in GLS, MD, electrocardiographic repolarization parameters, and hs-cTnI during the first 6 months of treatment.
Keywords: brain natriuretic peptide; cardiac toxicity; left ventricular function; myocardial strain; transthoracic echocardiography.
© 2021 The Authors. Echocardiographypublished by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Salem J‐E, Alexandre J, Bachelot A, et al Influence of steroid hormones on ventricular repolarization. Pharmacol Ther. 2016;167:38‐47. - PubMed
-
- Basaria S. Cardiovascular disease associated with androgen‐deprivation therapy: time to give it due respect. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(11):1232‐1234. - PubMed
-
- Tsai HK, D'Amico AV, Sadetsky N, et al Androgen deprivation therapy for localized prostate cancer and the risk of cardiovascular mortality. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99(20):1516‐1524. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

