The performance of the Xpert Bladder Cancer Monitor Test and voided urinary cytology in the follow-up of urinary bladder tumors
- PMID: 33764701
- PMCID: PMC8042818
- DOI: 10.2478/raon-2020-0072
The performance of the Xpert Bladder Cancer Monitor Test and voided urinary cytology in the follow-up of urinary bladder tumors
Abstract
Background: Cystoscopy in complement with urinary cytology represents the gold standard for the follow-up of patients with urinary bladder tumours. Xpert Bladder Cancer Monitor Test (XBC) is a novel mRNA-based urine test for bladder cancer surveillance. The aim of the study was to evaluate the performance of the XBC and voided urinary cytology (VUC) in the follow-up of bladder tumours.
Patients and methods: The XBC was performed on stabilized voided urine and VUC was performed on urine samples. The results were compared to cystoscopic findings and histopathological results after transurethral resection of the bladder lesion.
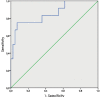
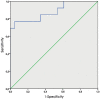
Results: For the prediction of malignant histopathological result sensitivity, the specificity and negative predictive value were 76.9%, 9 7.5% and 93.0% for the XBC and 38.4%, 9 7.5% and 83.3%, respectively for VUC. For the prediction of suspicious or positive cystoscopic finding sensitivity, the specificity and negative predictive value were 75.0%, 95.2%, and 93.0% respectively for the XBC and 41.7%, 97.6%, and 85.4% for VUC. The sensitivities for papilary urothelial neoplasms of low malignant potential (PUNLMP), low- and high-grade tumours were 0.0%, 66.7% an d 100.0% for the XBC and 0.0%, 66 .7% and 42.9%, respectively for VUC.
Conclusions: The XBC showed significantly higher overall sensitivity and negative predictive value than VUC and could be used to increase the recommended follow-up cystoscopy time intervals. Complementing the XBC and voided urinary cytology does not improve performance in comparison to the XBC alone.
Keywords: Xpert BC Monitor Test; cystoscopy; urinary bladder neoplasm; voided urinary cytology.
© 2021 Tomaz Smrkolj, Urska Cegovnik Primozic, Teja Fabjan, Sasa Sterpin, Josko Osredkar, published by Sciendo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prospective Validation of an mRNA-based Urine Test for Surveillance of Patients with Bladder Cancer.Eur Urol. 2019 May;75(5):853-860. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.11.055. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Eur Urol. 2019. PMID: 30553612
-
mRNA-Based Urine Test Performance in High and Very-High Risk Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Patients Undergoing Contextual Endoscopic Follow-up (VERNAL: Vesical Tumor Early Monitoring: mRNA-Based Follow-up).Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2025 Jun;23(3):102333. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2025.102333. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40199157
-
A comparison of urinary nuclear matrix protein-22 and bladder tumour antigen tests with voided urinary cytology in detecting and following bladder cancer: the prognostic value of false-positive results.BJU Int. 2001 Nov;88(7):692-701. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2001.02355.x. BJU Int. 2001. PMID: 11890239
-
Urinary markers in the everyday diagnosis of bladder cancer.Urologia. 2013 Sep-Dec;80(4):265-75. doi: 10.5301/urologia.5000041. Epub 2013 Nov 29. Urologia. 2013. PMID: 24419920 Review.
-
Replacing cystoscopy by urine markers in the follow-up of patients with low-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer?-An International Bladder Cancer Network project.Urol Oncol. 2016 Oct;34(10):452-9. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jul 2. Urol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27381893 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Novel Bladder Cancer Diagnostic and Surveillance Biomarkers-What Should a Urologist Really Know?Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Aug 5;19(15):9648. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19159648. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35955004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bladder cancer detection in patients with neurogenic bladder: are cystoscopy and cytology effective, and are biomarkers pertinent as future diagnostic tools? A scoping review.World J Urol. 2022 Aug;40(8):1897-1913. doi: 10.1007/s00345-022-03943-2. Epub 2022 Feb 4. World J Urol. 2022. PMID: 35119523
-
Clinical Evaluation of Two Non-Invasive Genetic Tests for Detection and Monitoring of Urothelial Carcinoma: Validation of UroVysion and Xpert Bladder Cancer Detection Test.Front Genet. 2022 Jun 6;13:839598. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.839598. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35734425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mariappan P, Fineron P, O’Donnell M, Gailer RM, Watson DJ, Smith G. Combining two grading systems: the clinical validity and inter-observer variability of the 1973 and 2004 WHO bladder cancer classification systems assessed in a UK cohort with 15 years of prospective follow-up. World J Urol. 2020. et al. Ahead of print. doi. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Babjuk M, Burger M, Compérat E, Gontero P, Mostafid AH, Palou J. European Association of Urology Guidelines 2020 Edition. Arnhem, The Netherlands: European Association of Urology Guidelines Office; 2020. EAU Guidelines on non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (TaT1 and CIS) 2020. et al. Presented at the EAU Annual Congress Amsterdam 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous