In the long shadow of our best intentions: Model-based assessment of the consequences of school reopening during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 33765026
- PMCID: PMC7993767
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248509
In the long shadow of our best intentions: Model-based assessment of the consequences of school reopening during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
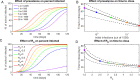
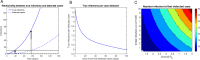
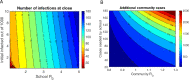
As the world grapples with the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, a particularly thorny set of questions surrounds the reopening of primary and secondary (K-12) schools. The benefits of in-person learning are numerous, in terms of education quality, mental health, emotional well-being, equity and access to food and shelter. Early reports suggested that children might have reduced susceptibility to COVID-19, and children have been shown to experience fewer complications than older adults. Over the past few months, our understanding of COVID-19 has been further shaped by emerging data, and it is now understood that children are as susceptible to infection as adults and have a similar viral load during infection, even if asymptomatic. Based on this updated understanding of the disease, we have used epidemiological modeling to explore the feasibility and consequences of school reopening in the face of differing rates of COVID-19 prevalence and transmission. We focused our analysis on the United States, but the results are applicable to other countries as well. We demonstrate the potential for a large discrepancy between detected cases and true infections in schools due to the combination of high asymptomatic rates in children coupled with delays in seeking testing and receiving results from diagnostic tests. Our findings indicate that, regardless of the initial prevalence of the disease, and in the absence of robust surveillance testing and contact-tracing, most schools in the United States can expect to remain open for 20-60 days without the emergence of sizeable disease clusters. At this point, even if schools choose to close after outbreaks occur, COVID-19 cases will be seeded from these school clusters and amplified into the community. Thus, our findings suggest that the debate between the risks to student safety and benefits of in-person learning frames a false dual choice. Reopening schools without surveillance testing and contact tracing measures in place will lead to spread within the schools and within the communities that eventually forces a return to remote learning and leaves a trail of infection in its wake.
Conflict of interest statement
AC and MS are employees of Fractal Therapeutics, Inc, and AC, MS, RN and DEW are shareholders in Fractal Therapeutics, Inc. RN is a shareholder of Halozyme Therapeutics, Inc. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials. Neither organization has a commercial interest in any products or services related to the subject of this paper (the implications of school reopening without adequate surveillance testing). The authors have no other commercial competing interests to declare. AC, NH and RN are parents of school and preschool-age children, and thus have a personal competing interest in the topic of this paper. All authors are members of the community, and thus have a personal stake in the topic of this paper given the current circumstances.
Figures
References
-
- Viner R. M. et al. , “Susceptibility to and transmission of COVID-19 amongst children and adolescents compared with adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis,” medRxiv, p. 2020.05.20.20108126, 2020.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

