Development and performance of CUHAS-ROBUST application for pulmonary rifampicin-resistance tuberculosis screening in Indonesia
- PMID: 33765092
- PMCID: PMC7993842
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249243
Development and performance of CUHAS-ROBUST application for pulmonary rifampicin-resistance tuberculosis screening in Indonesia
Abstract
Background and objectives: Diagnosis of Pulmonary Rifampicin Resistant Tuberculosis (RR-TB) with the Drug-Susceptibility Test (DST) is costly and time-consuming. Furthermore, GeneXpert for rapid diagnosis is not widely available in Indonesia. This study aims to develop and evaluate the CUHAS-ROBUST model performance, an artificial-intelligence-based RR-TB screening tool.
Methods: A cross-sectional study involved suspected all type of RR-TB patients with complete sputum Lowenstein Jensen DST (reference) and 19 clinical, laboratory, and radiology parameter results, retrieved from medical records in hospitals under the Faculty of Medicine, Hasanuddin University Indonesia, from January 2015-December 2019. The Artificial Neural Network (ANN) models were built along with other classifiers. The model was tested on participants recruited from January 2020-October 2020 and deployed into CUHAS-ROBUST (index test) application. Sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were obtained for assessment.
Results: A total of 487 participants (32 Multidrug-Resistant/MDR 57 RR-TB, 398 drug-sensitive) were recruited for model building and 157 participants (23 MDR and 21 RR) in prospective testing. The ANN full model yields the highest values of accuracy (88% (95% CI 85-91)), and sensitivity (84% (95% CI 76-89)) compare to other models that show sensitivity below 80% (Logistic Regression 32%, Decision Tree 44%, Random Forest 25%, Extreme Gradient Boost 25%). However, this ANN has lower specificity among other models (90% (95% CI 86-93)) where Logistic Regression demonstrates the highest (99% (95% CI 97-99)). This ANN model was selected for the CUHAS-ROBUST application, although still lower than the sensitivity of global GeneXpert results (87.5%).
Conclusion: The ANN-CUHAS ROBUST outperforms other AI classifiers model in detecting all type of RR-TB, and by deploying into the application, the health staff can utilize the tool for screening purposes particularly at the primary care level where the GeneXpert examination is not available.
Trial registration: NCT04208789.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

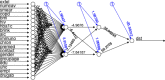
References
-
- WHO. WHO consolidated guidelines on drug-resistant tuberculosis treatment. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019.
-
- Kaur R, Jindal N, Arora S, Kataria S. Epidemiology of Rifampicin Resistant Tuberculosis and Common Mutations in rpoB Gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A Retrospective Study from Six Districts of Punjab (India) Using Xpert MTB/RIF Assay. J Lab Physicians. 2016;8(2):96–100. 10.4103/0974-2727.180789 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Orlando S, Triulzi I, Ciccacci F, Palla I, Palombi L, Marazzi MC, et al. Delayed diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis in HIV+ patients in Mozambique: A cost-effectiveness analysis of screening protocols based on four symptom screening, smear microscopy, urine LAM test and Xpert MTB/RIF. PLoS One. 2018;13(7):e0200523. 10.1371/journal.pone.0200523 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

