Nonpeptidergic neurons suppress mast cells via glutamate to maintain skin homeostasis
- PMID: 33765440
- PMCID: PMC8052305
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.002
Nonpeptidergic neurons suppress mast cells via glutamate to maintain skin homeostasis
Abstract
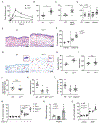
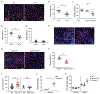
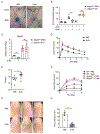
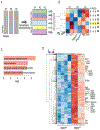
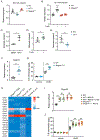
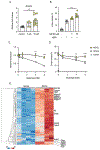
Cutaneous mast cells mediate numerous skin inflammatory processes and have anatomical and functional associations with sensory afferent neurons. We reveal that epidermal nerve endings from a subset of sensory nonpeptidergic neurons expressing MrgprD are reduced by the absence of Langerhans cells. Loss of epidermal innervation or ablation of MrgprD-expressing neurons increased expression of a mast cell gene module, including the activating receptor, Mrgprb2, resulting in increased mast cell degranulation and cutaneous inflammation in multiple disease models. Agonism of MrgprD-expressing neurons reduced expression of module genes and suppressed mast cell responses. MrgprD-expressing neurons released glutamate which was increased by MrgprD agonism. Inhibiting glutamate release or glutamate receptor binding yielded hyperresponsive mast cells with a genomic state similar to that in mice lacking MrgprD-expressing neurons. These data demonstrate that MrgprD-expressing neurons suppress mast cell hyperresponsiveness and skin inflammation via glutamate release, thereby revealing an unexpected neuroimmune mechanism maintaining cutaneous immune homeostasis.
Keywords: Langerhans cell; Mas-related G protein receptors; MrgprB2; MrgprD; S. aureus, beta-alanine; glutamate; kainate receptors; mast cell; neuroimmunology; nonpeptidergic neurons; skin.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests D.H.K. has a patent pending for the use of β-ala to suppress MC activation in disease states. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Neu(ronal) custodians of cutaneous immunity.Cell. 2021 Apr 15;184(8):1968-1970. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.040. Cell. 2021. PMID: 33861962
References
-
- Beaudry H, Daou I, Ase AR, Ribeiro-da-Silva A, and Seguela P (2017). Distinct behavioral responses evoked by selective optogenetic stimulation of the major TRPV1+ and MrgD+ subsets of C-fibers. Pain 158, 2329–2339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

