Efficacy of the self-mutual-group model targeting quality of life improvement among empty-nest older adults in Taiyuan, China: an intervention study
- PMID: 33765930
- PMCID: PMC7992987
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-021-02155-4
Efficacy of the self-mutual-group model targeting quality of life improvement among empty-nest older adults in Taiyuan, China: an intervention study
Abstract
Background: In China, more and more older people have encountered a situation called "empty nest." Meanwhile, the health status of empty-nest older adults is an increasing public health concern. This research aims to examine the effectiveness of Self-Mutual-Group (SMG) model in improving quality of life of the empty-nest older adults to provide a scientific evidence for improving their health.
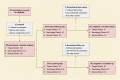
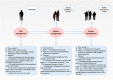
Methods: A prospective intervention study was conducted among empty-nest older adults in Taiyuan, Shanxi. Multi-stage stratified random cluster sampling was employed to selected participants. A total of 396 empty nesters were enrolled as participants, of which 204 and 192 were in the intervention and control group, respectively. The intervention group received a seven-month SMG-based intervention. A participant's quality of life was measured at the baseline and seven months after using the Short Form 36-Item Health Survey (SF-36).
Results: No significant difference was found between the intervention and control groups in terms of participant characteristics at baseline (P > 0.05). After the intervention, participants' scores on Mental Component Summary (MCS), Physical Component Summary (PCS), role emotional (RE), vitality (VT), social function (SF), mental health (MH) and general health (GH) increased significantly in the intervention group. Additionally, these scores differed significantly from those in the control group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: This study showed that the SMG-based health management is effective in improving quality of life among empty-nest older adults after seven months.
Trial registration: Study on the 'SMG' Health Management Model Based on Community Organization Theory among empty-nest older adults ( ChiCTR1800015884 ). Registration date: 26-04-2018. Retrospectively registered.
Keywords: Empty-nest older adults; Health management model; Intervention study; Quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang CC, Zhao HN, Zhu RF, et al. Improvement of social support in empty-nest elderly: results from an intervention study based on the self-mutual-group model. 2018. - PubMed
-
- Browning C. Excerpts of 2007 Beijing international academic summit of general practice——the role of general practitioners in promoting health ageing. Chinese General Practice. 2007;10:1131–1132.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources