The Arab region's contribution to global COVID-19 research: Bibliometric and visualization analysis
- PMID: 33766073
- PMCID: PMC7993895
- DOI: 10.1186/s12992-021-00690-8
The Arab region's contribution to global COVID-19 research: Bibliometric and visualization analysis
Abstract
Background: At the global level and in the Arab world, particularly in low-income countries, COVID-19 remains a major public health issue. As demonstrated by an incredible number of COVID-19-related publications, the research science community responded rapidly. Therefore, this study was intended to assess the growing contribution of the Arab world to global research on COVID-19.
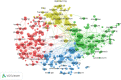
Methods: For the period between December 2019 and March 2021, the search for publications was conducted via the Scopus database using terms linked to COVID-19. VOSviewer 1.6.16 software was applied to generate a network map to assess hot topics in this area and determine the collaboration patterns between different countries. Furthermore, the research output of Arab countries was adjusted in relation to population size and gross domestic product (GDP).
Results: A total of 143,975 publications reflecting the global overall COVID-19 research output were retrieved. By restricting analysis to the publications published by the Arab countries, the research production was 6131 documents, representing 4.26% of the global research output regarding COVID-19. Of all these publications, 3990 (65.08%) were original journal articles, 980 (15.98%) were review articles, 514 (8.38%) were letters and 647 (10.55%) were others, such as editorials or notes. The highest number of COVID-19 publications was published by Saudi Arabia (n = 2186, 35.65%), followed by Egypt (n = 1281, 20.78%) and the United Arab Emirates (UAE), (n = 719, 11.73%). After standardization by population size and GDP, Saudi Arabia, UAE and Lebanon had the highest publication productivity. The collaborations were mostly with researchers from the United States (n = 968), followed by the United Kingdom (n = 661). The main research lines identified in COVID-19 from the Arab world are related to: public health and epidemiology; immunological and pharmaceutical research; signs, symptoms and clinical diagnosis; and virus detection.
Conclusions: A novel analysis of the latest Arab COVID-19-related studies is discussed in the current study and how these findings are connected to global production. Continuing and improving future collaboration between developing and developed countries will also help to facilitate the sharing of responsibilities for COVID-19 in research results and the implementation of policies for COVID-19.
Keywords: Arab world; Bibliometric; COVID-19; Novel coronavirus; Scopus.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that he has no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Contribution of Saudi Arabia to regional and global publications on COVID-19-related research: A bibliometric and visualization analysis.J Infect Public Health. 2022 Jul;15(7):709-719. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2022.05.013. Epub 2022 May 27. J Infect Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35667303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arab world's growing contribution to global leishmaniasis research (1998-2017): a bibliometric study.BMC Public Health. 2019 May 22;19(1):625. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-6969-9. BMC Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31118003 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the landscape of medical research in the Arab world countries: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis.Saudi Med J. 2024 Apr;45(4):387-396. doi: 10.15537/smj.2024.45.4.20230968. Saudi Med J. 2024. PMID: 38657984 Free PMC article.
-
Nursing and midwifery research activity in Arab countries from 1950 to 2017.BMC Health Serv Res. 2019 May 28;19(1):340. doi: 10.1186/s12913-019-4178-y. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019. PMID: 31138250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Benchmarking the scientific output of industrial wastewater research in Arab world by utilizing bibliometric techniques.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 May;23(10):10288-300. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6434-6. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 26996912 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Contribution of Saudi Arabia to regional and global publications on COVID-19-related research: A bibliometric and visualization analysis.J Infect Public Health. 2022 Jul;15(7):709-719. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2022.05.013. Epub 2022 May 27. J Infect Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35667303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 Pandemic Related Research in Africa: Bibliometric Analysis of Scholarly Output, Collaborations and Scientific Leadership.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jul 7;18(14):7273. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18147273. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34299724 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric and Visualization Analysis of the Ecology of Men's Sexual and Reproductive Healthcare Research in MENA (1985-2022): Outputs, Trends, Shortcomings and Hotspots.Arab J Urol. 2022 Nov 4;21(2):82-93. doi: 10.1080/2090598X.2022.2141864. eCollection 2023. Arab J Urol. 2022. PMID: 37234677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global research trends on the links between the gut microbiome and cancer: a visualization analysis.J Transl Med. 2022 Feb 11;20(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03293-y. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35148757 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 Research Trend during the First Two Years of the Pandemic in the United Arab Emirates: A PRISMA-Compliant Bibliometric Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jun 24;19(13):7753. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19137753. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35805413 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak situation. 2021. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed March 9 2021).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

