ChrXq27.3 miRNA cluster functions in cancer development
- PMID: 33766100
- PMCID: PMC7992321
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-021-01910-0
ChrXq27.3 miRNA cluster functions in cancer development
Abstract
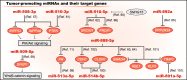
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate the expression of their target genes post-transcriptionally; thus, they are deeply involved in fundamental biological processes. miRNA clusters contain two or more miRNA-encoding genes, and these miRNAs are usually coexpressed due to common expression mechanisms. Therefore, miRNA clusters are effective modulators of biological pathways by the members coordinately regulating their multiple target genes, and an miRNA cluster located on the X chromosome q27.3 region has received much attention in cancer research recently. In this review, we discuss the novel findings of the chrXq27.3 miRNA cluster in various types of cancer.The chrXq27.3 miRNA cluster contains 30 mature miRNAs synthesized from 22 miRNA-encoding genes in an ~ 1.3-Mb region. The expressions of these miRNAs are usually negligible in many normal tissues, with the male reproductive system being an exception. In cancer tissues, each miRNA is dysregulated, compared with in adjacent normal tissues. The miRNA-encoding genes are not uniformly distributed in the region, and they are further divided into two groups (the miR-506-514 and miR-888-892 groups) according to their location on the genome. Most of the miRNAs in the former group are tumor-suppressive miRNAs that are further downregulated in various cancers compared with normal tissues. miR-506-3p in particular is the most well-known miRNA in this cluster, and it has various tumor-suppressive functions associated with the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, proliferation, and drug resistance. Moreover, other miRNAs, such as miR-508-3p and miR-509-3p, have similar tumor-suppressive effects. Hence, the expression of these miRNAs is clinically favorable as prognostic factors in various cancers. However, the functions of the latter group are less understood. In the latter group, miR-888-5p displays oncogenic functions, whereas miR-892b is tumor suppressive. Therefore, the functions of the miR-888-892 group are considered to be cell type- or tissue-specific.In conclusion, the chrXq27.3 miRNA cluster is a critical regulator of cancer progression, and the miRNAs themselves, their regulatory mechanisms, and their target genes might be promising therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Drug-resistance; Epithelial–mesenchymal transition; Proliferation; X chromosome; miR-506-3p; miR-888-5p; miRNA; miRNA cluster.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expression of the chrXq27.3 miRNA cluster in recurrent ovarian clear cell carcinoma and its impact on cisplatin resistance.Oncogene. 2021 Feb;40(7):1255-1268. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01595-3. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33420363 Free PMC article.
-
The microRNA-424/503 cluster: A master regulator of tumorigenesis and tumor progression with paradoxical roles in cancer.Cancer Lett. 2020 Dec 1;494:58-72. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.08.027. Epub 2020 Aug 23. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 32846190 Review.
-
NF-κB target microRNAs and their target genes in TNFα-stimulated HeLa cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1839(4):344-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.01.006. Epub 2014 Jan 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24418602
-
The clinical significance of downregulation of mir-124-3p, mir-146a-5p, mir-155-5p and mir-335-5p in gastric cancer tumorigenesis.Int J Oncol. 2014 Jul;45(1):197-208. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2415. Epub 2014 May 6. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24805774
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
Cited by
-
BGIG10116_34868: A Newly Discovered Gene Regulating Ejaculation Function.Front Physiol. 2022 Feb 28;13:762272. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.762272. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35295563 Free PMC article.
-
Impairment of RAD17 Functions by miR-506-3p as a Novel Synthetic Lethal Approach Targeting DNA Repair Pathways in Ovarian Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 18;12:923508. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.923508. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35924161 Free PMC article.
-
KIF2C accelerates the development of non-small cell lung cancer and is suppressed by miR-186-3p via the AKT-GSK3β-β-catenin pathway.Sci Rep. 2023 May 4;13(1):7288. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30073-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37142638 Free PMC article.
-
AGO2 protein: a key enzyme in the miRNA pathway as a novel biomarker in adrenocortical carcinoma.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2024 Nov 20;31(12):e240061. doi: 10.1530/ERC-24-0061. Print 2024 Dec 1. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39404265 Free PMC article.
-
The Expression of miR-205 in Prostate Carcinoma and the Relationship with Prognosis in Patients.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Aug 30;2022:1784791. doi: 10.1155/2022/1784791. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jul 26;2023:9846364. doi: 10.1155/2023/9846364. PMID: 36081431 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Kabekkodu SP, Shukla V, Varghese VK, Adiga D, Vethil Jishnu P, Chakrabarty S, et al. Cluster miRNAs and cancer: Diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic opportunities. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2020;11(2):e1563. 10.1002/wrna.1563. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

