Generation of SARS-CoV-2 reporter replicon for high-throughput antiviral screening and testing
- PMID: 33766889
- PMCID: PMC8053989
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2025866118
Generation of SARS-CoV-2 reporter replicon for high-throughput antiviral screening and testing
Abstract
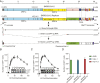
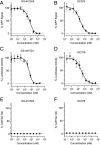
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) research and antiviral discovery are hampered by the lack of a cell-based virus replication system that can be readily adopted without biosafety level 3 (BSL-3) restrictions. Here, the construction of a noninfectious SARS-CoV-2 reporter replicon and its application in deciphering viral replication mechanisms and evaluating SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors are presented. The replicon genome is replication competent but does not produce progeny virions. Its replication can be inhibited by RdRp mutations or by known SARS-CoV-2 antiviral compounds. Using this system, a high-throughput antiviral assay has also been developed. Significant differences in potencies of several SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors in different cell lines were observed, which highlight the challenges of discovering antivirals capable of inhibiting viral replication in vivo and the importance of testing compounds in multiple cell culture models. The generation of a SARS-CoV-2 replicon provides a powerful platform to expand the global research effort to combat COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antivirals; high-throughput antiviral screening; replicon.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: All authors are employees of Merck and Company, Inc. A provisional patent application on the discoveries of this work has been filed.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

