Tissue-restricted control of established central nervous system autoimmunity by TNF receptor 2-expressing Treg cells
- PMID: 33766913
- PMCID: PMC8020675
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2014043118
Tissue-restricted control of established central nervous system autoimmunity by TNF receptor 2-expressing Treg cells
Abstract
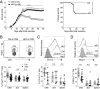
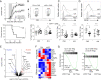
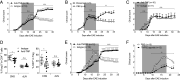
CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T (Treg) cells are central modulators of autoimmune diseases. However, the timing and location of Treg cell-mediated suppression of tissue-specific autoimmunity remain undefined. Here, we addressed these questions by investigating the role of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor 2 (TNFR2) signaling in Treg cells during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a model of multiple sclerosis. We found that TNFR2-expressing Treg cells were critical to suppress EAE at peak disease in the central nervous system but had no impact on T cell priming in lymphoid tissues at disease onset. Mechanistically, TNFR2 signaling maintained functional Treg cells with sustained expression of CTLA-4 and Blimp-1, allowing active suppression of pathogenic T cells in the inflamed central nervous system. This late effect of Treg cells was further confirmed by treating mice with TNF and TNFR2 agonists and antagonists. Our findings show that endogenous Treg cells specifically suppress an autoimmune disease by acting in the target tissue during overt inflammation. Moreover, they bring a mechanistic insight to some of the adverse effects of anti-TNF therapy in patients.
Keywords: TNF; Treg cells; autoimmune diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Cretney E., et al. ., The transcription factors Blimp-1 and IRF4 jointly control the differentiation and function of effector regulatory T cells. Nat. Immunol. 12, 304–311 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Wing J. B., Tanaka A., Sakaguchi S., Human FOXP3+ regulatory T cell heterogeneity and function in autoimmunity and cancer. Immunity 50, 302–316 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

