WWTR1(TAZ)-CAMTA1 reprograms endothelial cells to drive epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
- PMID: 33766984
- PMCID: PMC8015719
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.348221.120
WWTR1(TAZ)-CAMTA1 reprograms endothelial cells to drive epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
Abstract
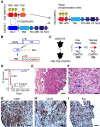
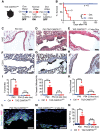
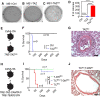
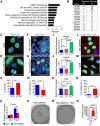
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EHE) is a poorly understood and devastating vascular cancer. Sequencing of EHE has revealed a unique gene fusion between the Hippo pathway nuclear effector TAZ (WWTR1) and the brain-enriched transcription factor CAMTA1 in ∼90% of cases. However, it remains unclear whether the TAZ-CAMTA1 gene fusion is a driver of EHE, and potential targeted therapies are unknown. Here, we show that TAZ-CAMTA1 expression in endothelial cells is sufficient to drive the formation of vascular tumors with the distinctive features of EHE, and inhibition of TAZ-CAMTA1 results in the regression of these vascular tumors. We further show that activated TAZ resembles TAZ-CAMTA1 in driving the formation of EHE-like vascular tumors, suggesting that constitutive activation of TAZ underlies the pathological features of EHE. We show that TAZ-CAMTA1 initiates an angiogenic and regenerative-like transcriptional program in endothelial cells, and disruption of the TAZ-CAMTA1-TEAD interaction or ectopic expression of a dominant negative TEAD in vivo inhibits TAZ-CAMTA1-mediated transformation. Our study provides the first genetic model of a TAZ fusion oncoprotein driving its associated human cancer, pinpointing TAZ-CAMTA1 as the key driver and a valid therapeutic target of EHE.
Keywords: CAMTA1; Hippo pathway; TAZ; YAP; cancer; endothelial cells; epithelioid hemangioendothelioma; gene fusion; vascular anomalies; vascular malformations.
© 2021 Driskill et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures



Similar articles
-
WWTR1(TAZ)-CAMTA1 gene fusion is sufficient to dysregulate YAP/TAZ signaling and drive epithelioid hemangioendothelioma tumorigenesis.Genes Dev. 2021 Apr 1;35(7-8):512-527. doi: 10.1101/gad.348220.120. Epub 2021 Mar 25. Genes Dev. 2021. PMID: 33766982 Free PMC article.
-
TAZ-CAMTA1 and YAP-TFE3 alter the TAZ/YAP transcriptome by recruiting the ATAC histone acetyltransferase complex.Elife. 2021 Apr 29;10:e62857. doi: 10.7554/eLife.62857. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33913810 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Hippo-YAP/TAZ Pathway in Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma and its Potential as a Therapeutic Target.Anticancer Res. 2024 Oct;44(10):4147-4153. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.17245. Anticancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39348982 Review.
-
Loss of CDKN2A Cooperates with WWTR1(TAZ)-CAMTA1 Gene Fusion to Promote Tumor Progression in Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma.Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Jul 5;29(13):2480-2493. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2497. Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36598859
-
Unraveling the Biology of Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma, a TAZ-CAMTA1 Fusion Driven Sarcoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 16;14(12):2980. doi: 10.3390/cancers14122980. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740643 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Matched Molecular and Clinical Analysis of the Epithelioid Haemangioendothelioma Cohort in the Stafford Fox Rare Cancer Program and Contextual Literature Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Sep 1;15(17):4378. doi: 10.3390/cancers15174378. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37686662 Free PMC article.
-
Control of stem cell renewal and fate by YAP and TAZ.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Dec;24(12):895-911. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00644-5. Epub 2023 Aug 25. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37626124 Review.
-
Gene Fusions as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Soft Tissue Sarcomas.Biomolecules. 2025 Jun 19;15(6):904. doi: 10.3390/biom15060904. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40563544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-Functional Regulation by YAP/TAZ Signaling Networks in Tumor Progression and Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Sep 24;15(19):4701. doi: 10.3390/cancers15194701. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma: Treatment Landscape and Innovations for an Ultra-Rare Sarcoma.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2025 Jun;26(6):516-523. doi: 10.1007/s11864-025-01328-2. Epub 2025 May 14. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40366525 Review.
References
-
- Arbiser JL, Larsson H, Claesson-Welsh L, Bai X, LaMontagne K, Weiss SW, Soker S, Flynn E, Brown LF. 2000. Overexpression of VEGF 121 in immortalized endothelial cells causes conversion to slowly growing angiosarcoma and high level expression of the VEGF receptors VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 in vivo. Am J Pathol 156: 1469–1476. 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65015-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
