Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase promotes LDL receptor shedding and accelerates the development of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 33767172
- PMCID: PMC7994674
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22167-3
Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase promotes LDL receptor shedding and accelerates the development of atherosclerosis
Abstract
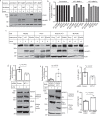
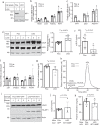
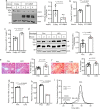
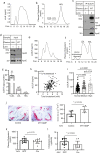
Plasma low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is primarily cleared by LDL receptor (LDLR). LDLR can be proteolytically cleaved to release its soluble ectodomain (sLDLR) into extracellular milieu. However, the proteinase responsible for LDLR cleavage is unknown. Here we report that membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) co-immunoprecipitates and co-localizes with LDLR and promotes LDLR cleavage. Plasma sLDLR and cholesterol levels are reduced while hepatic LDLR is increased in mice lacking hepatic MT1-MMP. Opposite effects are observed when MT1-MMP is overexpressed. MT1-MMP overexpression significantly increases atherosclerotic lesions, while MT1-MMP knockdown significantly reduces cholesteryl ester accumulation in the aortas of apolipoprotein E (apoE) knockout mice. Furthermore, sLDLR is associated with apoB and apoE-containing lipoproteins in mouse and human plasma. Plasma levels of sLDLR are significantly increased in subjects with high plasma LDL cholesterol levels. Thus, we demonstrate that MT1-MMP promotes ectodomain shedding of hepatic LDLR, thereby regulating plasma cholesterol levels and the development of atherosclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

