Risk of QT prolongation through drug interactions between hydroxychloroquine and concomitant drugs prescribed in real world practice
- PMID: 33767276
- PMCID: PMC7994840
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-86321-z
Risk of QT prolongation through drug interactions between hydroxychloroquine and concomitant drugs prescribed in real world practice
Abstract
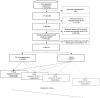
Hydroxychloroquine has recently received attention as a treatment for COVID-19. However, it may prolong the QTc interval. Furthermore, when hydroxychloroquine is administered concomitantly with other drugs, it can exacerbate the risk of QT prolongation. Nevertheless, the risk of QT prolongation due to drug-drug interactions (DDIs) between hydroxychloroquine and concomitant medications has not yet been identified. To evaluate the risk of QT prolongation due to DDIs between hydroxychloroquine and 118 concurrent drugs frequently used in real-world practice, we analyzed the electrocardiogram results obtained for 447,632 patients and their relevant electronic health records in a tertiary teaching hospital in Korea from 1996 to 2018. We repeated the case-control analysis for each drug. In each analysis, we performed multiple logistic regression and calculated the odds ratio (OR) for each target drug, hydroxychloroquine, and the interaction terms between those two drugs. The DDIs were observed in 12 drugs (trimebutine, tacrolimus, tramadol, rosuvastatin, cyclosporin, sulfasalazine, rofecoxib, diltiazem, piperacillin/tazobactam, isoniazid, clarithromycin, and furosemide), all with a p value of < 0.05 (OR 1.70-17.85). In conclusion, we found 12 drugs that showed DDIs with hydroxychloroquine in the direction of increasing QT prolongation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Administration USFaD. Who coronavirus disease (covid-19) dashboard. 2020.
-
- Gao J, Tian Z, Yang X. Breakthrough: Chloroquine phosphate has shown apparent efficacy in treatment of covid-19 associated pneumonia in clinical studies. Biosci. Trends. 2020;20:20. - PubMed
-
- Roden DM, Harrington RA, Poppas A, Russo AM. Considerations for drug interactions on QTC in exploratory covid-19 (coronavirus disease 2019) treatment. Circulation. 2020;20:20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

