Hospitalisation for lower respiratory tract infection is associated with an increased incidence of acute myocardial infarction and stroke in tropical Northern Australia
- PMID: 33767312
- PMCID: PMC7994310
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-86301-3
Hospitalisation for lower respiratory tract infection is associated with an increased incidence of acute myocardial infarction and stroke in tropical Northern Australia
Abstract
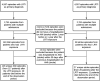
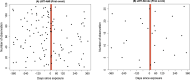
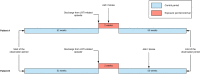
Acute respiratory infections appear to precipitate vascular events. Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and stroke are the leading cause of death and disability globally. This study was based on a cohort of patients admitted to Townsville University Hospital between January 2006 and December 2016. Using a self-controlled case series design, we investigated the risk of AMI or ischaemic stroke after an episode of pneumonia. We defined the 'risk interval' as the first 14 days after hospitalisation for pneumonia and the 'control interval' as one year before and one year after the risk interval. Among a population (N = 4557) with a median age of over 70, a total of 128 AMI and 27 stroke cases were identified within 1 year of an episode of pneumonia in this study. Ten and two admissions occurred during the risk interval, while 118 and 25 admissions occurred during the control period. The relative incidence ratios (RIR) of AMI increased after an episode of pneumonia (RIR=4.85, 95% confidence interval (CI) 2.44-9.67). The risk for stroke after the exposure period of 14 days was 4.94 (95% CI 1.12-21.78) considering only the first stroke incidence. The RIR results for AMI and stroke were not altered by adjusting for age, sex or Indigenous status. The risk of AMI and stroke were significantly higher two weeks after an episode of pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Roth GA, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N, Abbastabar H, Abd-Allah F, Abdela J, Abdelalim A. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1736–1788. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Krishnamurthi RV, Ikeda T, Feigin VL. Global, regional and country-specific burden of ischaemic stroke, intracerebral haemorrhage and subarachnoid haemorrhage: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Neuroepidemiology. 2020;54:171–179. doi: 10.1159/000506396. - DOI - PubMed
-
- James SL, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N, Abbastabar H, Abd-Allah F, Abdela J, Abdelalim A. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. The Lancet. 2018;392:1789–1858. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kaptoge S, Pennells L, De Bacquer D, Cooney MT, Kavousi M, Stevens G, Riley LM, Savin S, Khan T, Altay S. World Health Organization cardiovascular disease risk charts: Revised models to estimate risk in 21 global regions. Lancet Glob. Health. 2019;7:e1332–e1345. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30318-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical