Optimal treatment recommendations for diabetes patients using the Markov decision process along with the South Korean electronic health records
- PMID: 33767324
- PMCID: PMC7994640
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-86419-4
Optimal treatment recommendations for diabetes patients using the Markov decision process along with the South Korean electronic health records
Abstract
The extensive utilization of electronic health records (EHRs) and the growth of enormous open biomedical datasets has readied the area for applications of computational and machine learning techniques to reveal fundamental patterns. This study's goal is to develop a medical treatment recommendation system using Korean EHRs along with the Markov decision process (MDP). The sharing of EHRs by the National Health Insurance Sharing Service (NHISS) of Korea has made it possible to analyze Koreans' medical data which include treatments, prescriptions, and medical check-up. After considering the merits and effectiveness of such data, we analyzed patients' medical information and recommended optimal pharmaceutical prescriptions for diabetes, which is known to be the most burdensome disease for Koreans. We also proposed an MDP-based treatment recommendation system for diabetic patients to help doctors when prescribing diabetes medications. To build the model, we used the 11-year Korean NHISS database. To overcome the challenge of designing an MDP model, we carefully designed the states, actions, reward functions, and transition probability matrices, which were chosen to balance the tradeoffs between reality and the curse of dimensionality issues.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
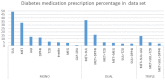
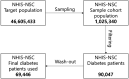


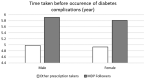
References
-
- Schaefer, A., Bailey, M., Shechter, S. & Roberts,, M. Modeling medical treatment using Markov decision processes. In Operations Research and Health Care 593–612 (2005).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

