LYTACs that engage the asialoglycoprotein receptor for targeted protein degradation
- PMID: 33767387
- PMCID: PMC8387313
- DOI: 10.1038/s41589-021-00770-1
LYTACs that engage the asialoglycoprotein receptor for targeted protein degradation
Abstract
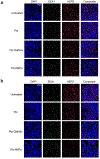
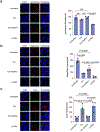
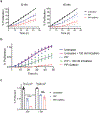
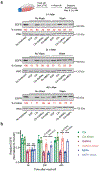
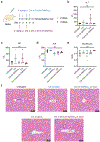
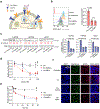
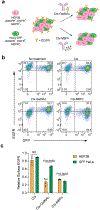
Selective protein degradation platforms have afforded new development opportunities for therapeutics and tools for biological inquiry. The first lysosome-targeting chimeras (LYTACs) targeted extracellular and membrane proteins for degradation by bridging a target protein to the cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor (CI-M6PR). Here, we developed LYTACs that engage the asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR), a liver-specific lysosome-targeting receptor, to degrade extracellular proteins in a cell-type-specific manner. We conjugated binders to a triantenerrary N-acetylgalactosamine (tri-GalNAc) motif that engages ASGPR to drive the downregulation of proteins. Degradation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) by GalNAc-LYTAC attenuated EGFR signaling compared to inhibition with an antibody. Furthermore, we demonstrated that a LYTAC consisting of a 3.4-kDa peptide binder linked to a tri-GalNAc ligand degrades integrins and reduces cancer cell proliferation. Degradation with a single tri-GalNAc ligand prompted site-specific conjugation on antibody scaffolds, which improved the pharmacokinetic profile of GalNAc-LYTACs in vivo. GalNAc-LYTACs thus represent an avenue for cell-type-restricted protein degradation.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc. part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
Stanford University has filed patent applications relating to lysosome targeting chimeras which are licensed to Lycia Therapeutics, listing G.A., S.M.B., and C.R.B. as co-inventors. G.A., S.M.B., C.L.M., J.R.C., and C.R.B. are co-inventors on a patent application relating to PIP-LYTACs filed by Stanford University (docket number STAN-1780PRV). C.R.B. is a co-founder and Scientific Advisory Board member of Lycia Therapeutics, Palleon Pharmaceuticals, Enable Bioscience, Redwood Biosciences (a subsidiary of Catalent), and InterVenn Biosciences, and a member of the Board of Directors of Eli Lilly & Company. J.R.C. is a founder of xCella Biosciences and Combangio Inc. and co-founder and director of Trapeze Therapeutics.
Figures




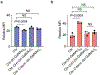


Comment in
-
Lysosome-targeting chimeras evolve.Nat Chem Biol. 2021 Sep;17(9):931-933. doi: 10.1038/s41589-021-00835-1. Nat Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 34413526 No abstract available.
References
-
- Krönke J, Udeshi ND, Narla A, Grauman P, Hurst SN, McConkey M, Svinkina T, Heckl D, Comer E, Li X, Ciarlo C, Hartman E, Munshi N, Schenone M, Schreiber SL, Carr SA & Ebert BL Lenalidomide Causes Selective Degradation of IKZF1 and IKZF3 in Multiple Myeloma Cells. Science 343, 301–305 (2014). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nabet B, Roberts JM, Buckley DL, Paulk J, Dastjerdi S, Yang A, Leggett AL, Erb MA, Lawlor MA, Souza A, Scott TG, Vittori S, Perry JA, Qi J, Winter GE, Wong K-K, Gray NS & Bradner JE The dTAG system for immediate and target-specific protein degradation. Nat. Chem. Biol 14, 431–441 (2018). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

