The tumor suppressor kinase DAPK3 drives tumor-intrinsic immunity through the STING-IFN-β pathway
- PMID: 33767426
- PMCID: PMC8300883
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-021-00896-3
The tumor suppressor kinase DAPK3 drives tumor-intrinsic immunity through the STING-IFN-β pathway
Abstract
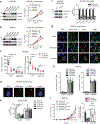
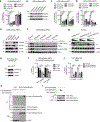
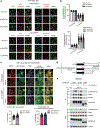
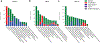
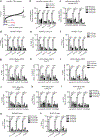
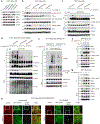
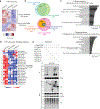
Evasion of host immunity is a hallmark of cancer; however, mechanisms linking oncogenic mutations and immune escape are incompletely understood. Through loss-of-function screening of 1,001 tumor suppressor genes, we identified death-associated protein kinase 3 (DAPK3) as a previously unrecognized driver of anti-tumor immunity through the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway of cytosolic DNA sensing. Loss of DAPK3 expression or kinase activity impaired STING activation and interferon (IFN)-β-stimulated gene induction. DAPK3 deficiency in IFN-β-producing tumors drove rapid growth and reduced infiltration of CD103+CD8α+ dendritic cells and cytotoxic lymphocytes, attenuating the response to cancer chemo-immunotherapy. Mechanistically, DAPK3 coordinated post-translational modification of STING. In unstimulated cells, DAPK3 inhibited STING K48-linked poly-ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation. After cGAMP stimulation, DAPK3 was required for STING K63-linked poly-ubiquitination and STING-TANK-binding kinase 1 interaction. Comprehensive phospho-proteomics uncovered a DAPK3-specific phospho-site on the E3 ligase LMO7, critical for LMO7-STING interaction and STING K63-linked poly-ubiquitination. Thus, DAPK3 is an essential kinase for STING activation that drives tumor-intrinsic innate immunity and tumor immune surveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors state that they have no competing interests. Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to S.S. (
Figures










References
-
- Zitvogel L, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Smyth MJ & Kroemer G Type I interferons in anticancer immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 15, 405–414 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Vanpouille-Box C, Demaria S, Formenti SC & Galluzzi L Cytosolic DNA Sensing in Organismal Tumor Control. Cancer Cell 34, 361–378 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Chen Q, Sun L & Chen ZJ Regulation and function of the cGAS-STING pathway of cytosolic DNA sensing. Nat Immunol 17, 1142–1149 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

