Neuronal enhancers are hotspots for DNA single-strand break repair
- PMID: 33767446
- PMCID: PMC9827709
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03468-5
Neuronal enhancers are hotspots for DNA single-strand break repair
Abstract
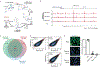
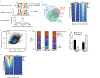
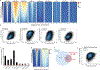
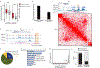
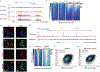
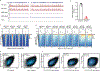
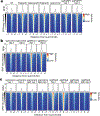
Defects in DNA repair frequently lead to neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative diseases, underscoring the particular importance of DNA repair in long-lived post-mitotic neurons1,2. The cellular genome is subjected to a constant barrage of endogenous DNA damage, but surprisingly little is known about the identity of the lesion(s) that accumulate in neurons and whether they accrue throughout the genome or at specific loci. Here we show that post-mitotic neurons accumulate unexpectedly high levels of DNA single-strand breaks (SSBs) at specific sites within the genome. Genome-wide mapping reveals that SSBs are located within enhancers at or near CpG dinucleotides and sites of DNA demethylation. These SSBs are repaired by PARP1 and XRCC1-dependent mechanisms. Notably, deficiencies in XRCC1-dependent short-patch repair increase DNA repair synthesis at neuronal enhancers, whereas defects in long-patch repair reduce synthesis. The high levels of SSB repair in neuronal enhancers are therefore likely to be sustained by both short-patch and long-patch processes. These data provide the first evidence of site- and cell-type-specific SSB repair, revealing unexpected levels of localized and continuous DNA breakage in neurons. In addition, they suggest an explanation for the neurodegenerative phenotypes that occur in patients with defective SSB repair.
Figures


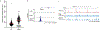





Comment in
-
Brain DNA damage hotspots.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021 May;22(5):304-305. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00367-5. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33828243 No abstract available.
-
Neuronal enhancers get a break.Neuron. 2021 Jun 2;109(11):1766-1768. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.05.008. Neuron. 2021. PMID: 34081919
-
Mapping the hotspots for DNA repair synthesis in human brain organoids.Cell Death Differ. 2021 Nov;28(11):3193-3195. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00863-3. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Cell Death Differ. 2021. PMID: 34465892 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Caldecott KW Single-strand break repair and genetic disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 9, 619– 631 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Miller MR & Chinault DN The roles of DNA polymerases alpha, beta, and gamma in DNA repair synthesis induced in hamster and human cells by different DNA damaging agents. J. Biol. Chem. 257, 10204–10209 (1982). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

