AKR1B10 confers resistance to radiotherapy via FFA/TLR4/NF-κB axis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PMID: 33767586
- PMCID: PMC7975703
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.52927
AKR1B10 confers resistance to radiotherapy via FFA/TLR4/NF-κB axis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Abstract
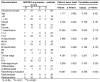
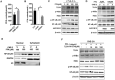
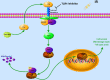
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is one kind of human head and neck cancers with high incidence in Southern China, Southeast Asia and North Africa. In spite of great innovations in radiation and chemotherapy treatments, the 5-year survival rate is not satisfactory. One of the main reasons is resistance to radiotherapy which leads to therapy failure and recurrence of NPC. The mechanism underlying remains to be fully elucidated. Aldo-keto reductase B10 (AKR1B10) plays a role in the formation and development of carcinomas. However, its role in resistance to radiotherapy of NPC is not clear. In this research, the relationships between AKR1B10 expression and the treatment effect of NPC patients, NPC cell survival, cell apoptosis, and DNA damage repair, as well as the effect and mechanism of AKR1B10 expression on NPC radioresistance were explored. A total of 58 paraffin tissues of NPC patients received radiotherapy were collected including 30 patients with radiosensitivity and 28 patients with radioresistance. The relationships between AKR1B10 expression and the treatment effect as well as clinical characteristics were analyzed by immuno-histochemical experiments, and the roles of AKR1B10 in cell survival, apoptosis and DNA damage repair were detected using the AKR1B10 overexpressed cell models. Furthermore the mechanism of AKR1B10 in NPC radioresistance was explored. Finally, the radioresistance effect of AKR1B10 expression was evaluated by the tumor xenograft model of nude mice and the method of radiotherapy. The results showed AKR1B10 expression level was correlated with radiotherapy resistance, and AKR1B10 overexpression promoted proliferation of NPC cells, reduced apoptosis and decreased cellular DNA damage after radiotherapy. The probable molecular mechanism is that AKR1B10 expression activated FFA/TLR4/NF-κB axis in NPC cells. This was validated by using the TLR4 inhibitor TAK242 to treat NPC cells with AKR1B10 expression, which reduced the phosphorylation of NF-κB. This study suggests that AKR1B10 can induce radiotherapy resistance and promote cell survival via FFA/TLR4/NF-κB axis in NPC, which may provide a novel target to fight against radiotherapy resistance of NPC.
Keywords: AKR1B10; FFA/TLR4/NF-κB axis; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; radiotherapy resistance.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-19b-3p regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiosensitivity by targeting TNFAIP3/NF-κB axis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Dec 5;35(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0465-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27919278 Free PMC article.
-
Low expression of Aldo-keto reductase 1B10 is a novel independent prognostic indicator for nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Cell Biosci. 2016 Mar 5;6:18. doi: 10.1186/s13578-016-0082-x. eCollection 2016. Cell Biosci. 2016. PMID: 26949513 Free PMC article.
-
CHAF1B induces radioresistance by promoting DNA damage repair in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Mar;123:109748. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109748. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31869663
-
The Role of Cyclin d1 in Radiotherapy Resistance of Advance Stage Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Systematic Review.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Jul 1;25(7):2211-2218. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.7.2211. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 39068551 Free PMC article.
-
Radio-Susceptibility of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Focus on Epstein- Barr Virus, MicroRNAs, Long Non-Coding RNAs and Circular RNAs.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2020;13(3):192-205. doi: 10.2174/1874467213666191227104646. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31880267 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of Licochalcone A on proliferation, invasion, and drug resistance of glioma cells by regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024 Dec 20;80:100542. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2024.100542. eCollection 2025. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024. PMID: 39708583 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB in Cell Deaths, Therapeutic Resistance and Nanotherapy of Tumors: Recent Advances.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 May 24;16(6):783. doi: 10.3390/ph16060783. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fatty acid metabolism: A new target for nasopharyngeal carcinoma therapy.Chin J Cancer Res. 2024 Dec 30;36(6):652-668. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2024.06.05. Chin J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39802901 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of aldo‑keto reductase family 1 member B10 in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Mol Clin Oncol. 2023 Sep 22;19(5):89. doi: 10.3892/mco.2023.2685. eCollection 2023 Nov. Mol Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37854325 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of AKR1B10 in Physiology and Pathophysiology.Metabolites. 2021 May 21;11(6):332. doi: 10.3390/metabo11060332. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34063865 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wei WI, Sham JS. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 2005;365:2041–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66698-6. - PubMed
-
- Al-Ejeh F, Kumar R, Wiegmans A, Lakhani SR, Brown MP, Khanna KK. Harnessing the complexity of DNA-damage response pathways to improve cancer treatment outcomes. Oncogene. 2010;29:6085–98. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.407. - PubMed
-
- Rogakou EP, Pilch DR, Orr AH. et al. DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:5858–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

