Immunogenicity Risk Profile of Nanobodies
- PMID: 33767701
- PMCID: PMC7985456
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.632687
Immunogenicity Risk Profile of Nanobodies
Abstract
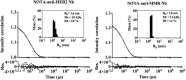
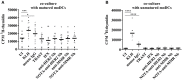
Nanobodies (Nbs), the variable domains of camelid heavy chain-only antibodies, are a promising class of therapeutics or in vivo imaging reagents entering the clinic. They possess unique characteristics, including a minimal size, providing fast pharmacokinetics, high-target specificity, and an affinity in the (sub-)nanomolar range in conjunction with an easy selection and production, which allow them to outperform conventional antibodies for imaging and radiotherapeutic purposes. As for all protein theranostics, extended safety assessment and investigation of their possible immunogenicity in particular are required. In this study, we assessed the immunogenicity risk profile of two Nbs that are in phase II clinical trials: a first Nb against Human Epidermal growth factor Receptor 2 (HER2) for PET imaging of breast cancer and a second Nb with specificity to the Macrophage Mannose Receptor (MMR) for PET imaging of tumor-associated macrophages. For the anti-HER2 Nb, we show that only one out of 20 patients had a low amount of pre-existing anti-drug antibodies (ADAs), which only marginally increased 3 months after administering the Nb, and without negative effects of safety and pharmacokinetics. Further in vitro immunogenicity assessment assays showed that both non-humanized Nbs were taken up by human dendritic cells but exhibited no or only a marginal capacity to activate dendritic cells or to induce T cell proliferation. From our data, we conclude that monomeric Nbs present a low immunogenicity risk profile, which is encouraging for their future development toward potential clinical applications.
One sentence summary: Nanobodies, the recombinant single domain affinity reagents derived from heavy chain-only antibodies in camelids, are proven to possess a low immunogenicity risk profile, which will facilitate a growing number of Nanobodies to enter the clinic for therapeutic or in vivo diagnostic applications.
Keywords: DC activation; T cell—DC interactions; anti drug antibodies; dendritic cells; immunogenicity; nanobody.
Copyright © 2021 Ackaert, Smiejkowska, Xavier, Sterckx, Denies, Stijlemans, Elkrim, Devoogdt, Caveliers, Lahoutte, Muyldermans, Breckpot and Keyaerts.
Conflict of interest statement
SD was employed by SD Analytics. ND, MK, and TL hold patents on the use of anti-HER2 and -MMR Nbs for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer and cardiovascular diseases. ND and TL are co-founder of, shareholder of and employed by or consultant for Precirix, a company that uses the anti-HER2 nanobody in radiotherapeutic applications. ND, MK, and TL are co-founder of Abscint who develops the anti-HER2 and anti-MMR Nb tracers for diagnostic purposes. ND has received funding from Boehringer-Ingelheim, Complix, Agenus, Confo Therapeutics, Roche, 121BIO, Agenus, Exevir, and Telix Pharma. MK, TL, ND, and CX have patents on Nb imaging and therapy. TL received honoraria from Precirix (consultant and board member), IBA (scientific advisor), and Institut des Radioéléments (IRE) (scientific advisor). The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Malucchi S, Bertolotto A. Clinical aspects of immunogenicity to biopharmaceuticalsno title. In: van de Weert M, Møller EH. editors. Immunogenicity of Biopharmaceuticals. Biotechnology: Pharmaceutical Aspects. (2008) Vol 8. New York, NY: Springer. 27 p.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

