Primary Borderline Mucinous Testicular Tumor: A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 33767975
- PMCID: PMC7986722
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.619774
Primary Borderline Mucinous Testicular Tumor: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
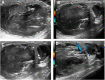
Primary mucinous tumors of the testis and paratestis are very rare, with only 29 reported cases detected in a PubMed search. The histopathological characteristics of primary testicular mucinous tumors are similar to their ovarian counterparts, and the diagnosis and naming criteria refer to the criteria for female ovarian mucinous tumors. However, the clinical and imaging features of primary testicular mucinous tumors are poorly understood, and they are thus frequently undiagnosed or misdiagnosed. We present the case of a patient with a primary testicular mucinous tumor. A 52-year-old man presented with a 1-year history of painless enlargement of the left scrotum. Ultrasound examination revealed a cystic mass in the left testis, with viscous fluid areas and calcified spots, irregular solid bulges on the cyst wall, and a small blood supply. Serum alpha-fetoprotein, β-human chorionic gonadotropin, lactate dehydrogenase, renal function, inflammatory markers, and routine urine and blood examinations were all normal. The patient underwent radical resection of the left testis. Postoperative pathology showed a multilocular cystic mass, with the inner wall of the sac lined with mucous columnar epithelial cells, some with mild nuclear atypia, and no interstitial infiltration. The pathological diagnosis was testicular mucinous tumor. Postoperative abdominal and pelvic computed tomography, colonoscopy, and gastroscopy showed no suspicious lesions. The final diagnosis was primary testicular borderline mucinous tumor. The patient underwent postoperative follow-up examinations once a year for 4 years. Serum tumor markers, scrotal ultrasound, abdominal and pelvic computed tomography scans, and colonoscopy and gastroscopy revealed no evidence of metastases or other primary adenocarcinoma. This case highlights the clinical and imaging characteristics of primary testicular mucinous tumors, which might aid their differential diagnosis.
Keywords: clinical characteristic; differential diagnosis; imaging characteristic; mucinous tumor; testis.
Copyright © 2021 Hao, Kang, Kang, Yu, Li and Xue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Case report: Misdiagnosis of primary mucinous cystadenoma of the testicle by ultrasound.Front Oncol. 2023 Sep 5;13:1206697. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1206697. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37731639 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Testicular Mucinous Adenocarcinoma-a Case Report and Review of Literature.Indian J Surg Oncol. 2024 Mar;15(1):125-128. doi: 10.1007/s13193-023-01832-7. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38511018 Free PMC article.
-
Primary mucinous tumors of the testis and paratestis: a report of nine cases.Am J Surg Pathol. 2003 Sep;27(9):1221-8. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200309000-00005. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12960806
-
[A case of papillary cystadenoma of the epididymis mimicking a testicular tumor].Hinyokika Kiyo. 2012 Jan;58(1):39-43. Hinyokika Kiyo. 2012. PMID: 22343743 Review. Japanese.
-
Immunohistochemistry as a diagnostic aid in the evaluation of ovarian tumors.Semin Diagn Pathol. 2005 Feb;22(1):3-32. doi: 10.1053/j.semdp.2005.11.002. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2005. PMID: 16512597 Review.
Cited by
-
Case report: Rare isolated cystic hepatic metastasis of a patient with squamous cell lung carcinoma history and the prognosis.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 27;12:986603. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.986603. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36387177 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: Misdiagnosis of primary mucinous cystadenoma of the testicle by ultrasound.Front Oncol. 2023 Sep 5;13:1206697. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1206697. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37731639 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic nutritional index and serum lactate dehydrogenase predict the prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients who received intensity-modulated radiation therapy.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Dec;149(20):17795-17805. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05485-5. Epub 2023 Nov 7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37934254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moch H, Cubilla AL, Humphrey PA, Reuter VE, Ulbright TM. WHO classification of tumours of the urinary systemand male genital organ. Lyon: IARC Press; (2016) p. 238–9p. - PubMed
-
- John N, Guido S, Jonathan I, Isabell A, et al. . WHO classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organ Vol. 216. Lyon: IARC Press; (2004). 261p.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

