The Prognostic Significance of Anisomycin-Activated Phospho-c-Jun NH2-Terminal Kinase (p-JNK) in Predicting Breast Cancer Patients' Survival Time
- PMID: 33768099
- PMCID: PMC7985183
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.656693
The Prognostic Significance of Anisomycin-Activated Phospho-c-Jun NH2-Terminal Kinase (p-JNK) in Predicting Breast Cancer Patients' Survival Time
Abstract
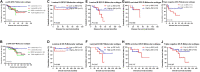
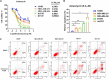
This study aims to investigate the prognostic significance of p-JNK in breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) and analyze the relationship between anisomycin, p-JNK. A total of 104 breast cancer patients had NACT were enrolled in this study. The western blot and immunohistochemistry assays were used to determine the protein expressions of p-JNK in human breast cancer cell lines and patients' cancer tissues. The chi-square test and Fisher's exact test were adopted to gauge the associations between breast cancer and clinicopathological variables by p-JNK expression, whereas the univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression models were used to analyze the prognostic value of p-JNK expression. The Kaplan-Meier plots and the log-rank test were adopted to determine patients' disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS). Findings indicated that the p-JNK expression had prognostic significance in univariate and multivariate Cox regression survival analyses. Results of log-rank methods showed that: (1) the mean DFS and OS times in patients with high p-JNK expression were significantly longer than those in patients with low p-JNK expression (χ2 = 5.908, P = 0.015 and χ2 = 6.593, P = 0.010, respectively). p-JNK expression is a significant prognostic factor that can effectively predict the survival in breast cancer patients receiving NACT. Treatment with the JNK agonist anisomycin can induce apoptosis, lead to increased p-JNK expression and decreased p-STAT3 expression. Moreover, the p-JNK expression was inversely correlated with p-STAT3 expression.
Keywords: anisomycin; breast cancer; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; p-JNK; p-STAT3.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Zhou, Kong, Su, Wang, Li, Luo, Liu, Fang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) in Patients With Breast Cancer Treated With Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy as a Useful Prognostic Indicator.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 30;9:656741. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.656741. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33859986 Free PMC article.
-
PD-L1 Protein Expression Is Associated With Good Clinical Outcomes and Nomogram for Prediction of Disease Free Survival and Overall Survival in Breast Cancer Patients Received Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy.Front Immunol. 2022 May 20;13:849468. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.849468. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35669769 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative Breast Immune Prognostic Index as Prognostic Factor Predicts the Clinical Outcomes of Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 7;13:831848. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.831848. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35320931 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment Systemic Inflammation Response Index in Patients with Breast Cancer Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy as a Useful Prognostic Indicator.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Mar 3;12:1543-1567. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S235519. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32184659 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of PD-L1 expression and NLR as prognostic marker in patients with surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer.J Cancer. 2019 Oct 22;10(26):6703-6710. doi: 10.7150/jca.34469. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31777599 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
JNK pathway suppression mediates insensitivity to combination endocrine therapy and CDK4/6 inhibition in ER+ breast cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Aug 19;44(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03466-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40826108 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Risk Model Based on Lipid Metabolism-Associated Genes Predicts Prognosis and Indicates Immune Microenvironment in Breast Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 14;9:691676. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.691676. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34195202 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the PKCζ/JNK signaling pathway in regulating the development of femoral head necrosis.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2025 Mar 3;58:e13771. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2025e13771. eCollection 2025. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2025. PMID: 40053032 Free PMC article.
-
Digital spatial profiling identifies phospho-JNK as a biomarker for early risk stratification of aggressive prostate cancer.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 5;15:1572299. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1572299. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40538844 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the role of RAC3 in the growth and invasion of cisplatin-resistant bladder cancer cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jun;28(11):e18473. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18473. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38847477 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asselain B., Barlow W., Bartlett J., Bergh J., Bergsten-Nordström E., Bliss J., et al. (2018). Long-term outcomes for neoadjuvant versus adjuvant chemotherapy in early breast cancer: meta-analysis of individual patient data from ten randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 19 27–39. 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30777-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

