Application of Machine Learning Algorithms to Predict Central Lymph Node Metastasis in T1-T2, Non-invasive, and Clinically Node Negative Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- PMID: 33768105
- PMCID: PMC7986413
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.635771
Application of Machine Learning Algorithms to Predict Central Lymph Node Metastasis in T1-T2, Non-invasive, and Clinically Node Negative Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Abstract
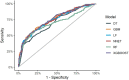
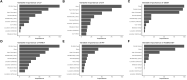
Purpose: While there are no clear indications of whether central lymph node dissection is necessary in patients with T1-T2, non-invasive, clinically uninvolved central neck lymph nodes papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC), this study seeks to develop and validate models for predicting the risk of central lymph node metastasis (CLNM) in these patients based on machine learning algorithms. Methods: This is a retrospective study comprising 1,271 patients with T1-T2 stage, non-invasive, and clinically node negative (cN0) PTC who underwent surgery at the Department of Endocrine and Breast Surgery of The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University from February 1, 2016, to December 31, 2018. We applied six machine learning (ML) algorithms, including Logistic Regression (LR), Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM), Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), Random Forest (RF), Decision Tree (DT), and Neural Network (NNET), coupled with preoperative clinical characteristics and intraoperative information to develop prediction models for CLNM. Among all the samples, 70% were randomly selected to train the models while the remaining 30% were used for validation. Indices like the area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC), sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were calculated to test the models' performance. Results: The results showed that ~51.3% (652 out of 1,271) of the patients had pN1 disease. In multivariate logistic regression analyses, gender, tumor size and location, multifocality, age, and Delphian lymph node status were all independent predictors of CLNM. In predicting CLNM, six ML algorithms posted AUROC of 0.70-0.75, with the extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) model standing out, registering 0.75. Thus, we employed the best-performing ML algorithm model and uploaded the results to a self-made online risk calculator to estimate an individual's probability of CLNM (https://jin63.shinyapps.io/ML_CLNM/). Conclusions: With the incorporation of preoperative and intraoperative risk factors, ML algorithms can achieve acceptable prediction of CLNM with Xgboost model performing the best. Our online risk calculator based on ML algorithm may help determine the optimal extent of initial surgical treatment for patients with T1-T2 stage, non-invasive, and clinically node negative PTC.
Keywords: central lymph node metastasis; lymph node dissections; machine learning algorithms; papillary thyroid carcinoma; prediction model.
Copyright © 2021 Zhu, Zheng, Li, Huang, Ren, Wang, Dai and Su.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LASSO-based machine learning models for the prediction of central lymph node metastasis in clinically negative patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 23;13:1030045. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1030045. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36506061 Free PMC article.
-
Model development to predict central lymph node metastasis in cN0 papillary thyroid microcarcinoma by machine learning.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Aug;10(16):892. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3594. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36111037 Free PMC article.
-
Interpretable machine learning model based on the systemic inflammation response index and ultrasound features can predict central lymph node metastasis in cN0T1-T2 papillary thyroid carcinoma.Gland Surg. 2023 Nov 24;12(11):1485-1499. doi: 10.21037/gs-23-349. Epub 2023 Nov 17. Gland Surg. 2023. PMID: 38107491 Free PMC article.
-
The incidence and risk factors for central lymph node metastasis in cN0 papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: a meta-analysis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;274(3):1327-1338. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4302-0. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 27645473 Review.
-
Meta-analysis of ultrasound for cervical lymph nodes in papillary thyroid cancer: Diagnosis of central and lateral compartment nodal metastases.Eur J Radiol. 2019 Mar;112:14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2019.01.006. Epub 2019 Jan 7. Eur J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30777203 Review.
Cited by
-
LASSO-based machine learning models for the prediction of central lymph node metastasis in clinically negative patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 23;13:1030045. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1030045. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36506061 Free PMC article.
-
PTC-MAS: A Deep Learning-Based Preoperative Automatic Assessment of Lymph Node Metastasis in Primary Thyroid Cancer.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 May 12;13(10):1723. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13101723. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37238205 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the best predictive models for early‑onset metastatic cancer: Insights and innovations (Review).Oncol Rep. 2024 Apr;51(4):60. doi: 10.3892/or.2024.8719. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Oncol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38456540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated analysis of single-cell, spatial and bulk RNA-sequencing identifies a cell-death signature for predicting the outcomes of head and neck cancer.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 7;15:1487966. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1487966. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39575251 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the influence of Circ_0059706 expression on prognosis in patients with acute myeloid leukemia using classical statistics and machine learning.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 21;13:961142. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.961142. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36338954 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

