Combined inhibition of Aurora-A and ATR kinase results in regression of MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma
- PMID: 33768209
- PMCID: PMC7610389
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-020-00171-8
Combined inhibition of Aurora-A and ATR kinase results in regression of MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma
Abstract
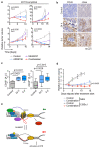
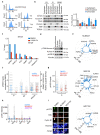
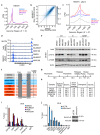
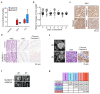
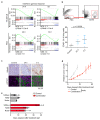
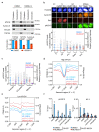
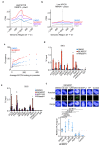
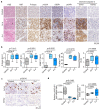
Amplification of MYCN is the driving oncogene in a subset of high-risk neuroblastoma. The MYCN protein and the Aurora-A kinase form a complex during S phase that stabilizes MYCN. Here we show that MYCN activates Aurora-A on chromatin, which phosphorylates histone H3 at serine 10 in S phase, promotes the deposition of histone H3.3 and suppresses R-loop formation. Inhibition of Aurora-A induces transcription-replication conflicts and activates the Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related (ATR) kinase, which limits double-strand break accumulation upon Aurora-A inhibition. Combined inhibition of Aurora-A and ATR induces rampant tumor-specific apoptosis and tumor regression in mouse models of neuroblastoma, leading to permanent eradication in a subset of mice. The therapeutic efficacy is due to both tumor cell-intrinsic and immune cell-mediated mechanisms. We propose that targeting the ability of Aurora-A to resolve transcription-replication conflicts is an effective therapy for MYCN-driven neuroblastoma (141 words).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Rickman DS, Schulte JH, Eilers M. The Expanding World of N-MYC-Driven Tumors. Cancer Discov. 2018;8:150–163. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0273. - DOI - PubMed
Additional References to Methods
-
- Boguslawski SJ, et al. Characterization of monoclonal antibody to DNA.RNA and its application to immunodetection of hybrids. Journal of immunological methods. 1986;89:123–130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

