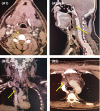
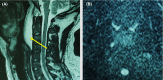
Retropharyngeal edema secondary to superior vena cava syndrome revealing Behcet's disease
- PMID: 33768866
- PMCID: PMC7981641
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.3800
Retropharyngeal edema secondary to superior vena cava syndrome revealing Behcet's disease
Abstract
Retropharyngeal edema, uncommon in superior vena cava syndrome, can exceptionally represent the first manifestation of Behcet's disease, which should be taken into account in the differential diagnosis of this condition.
Keywords: Behcet's disease; retropharyngeal edema; superior vena cava syndrome.
© 2021 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Ilter N, Senol E, Gurer MA, Oztas MO. Behçet's disease and HCV infection. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39(5):396‐397. - PubMed
-
- Kurihara N, Takahashi S, Higano S, Nakamura M, Tsuda M, Saito H. Edema in the retropharyngeal space associated with head and neck tumors: CT imaging characteristics. Neuroradiology. 2005;47:609‐615. - PubMed
-
- Hoang JK, Branstetter BF, Eastwood JD, Glastonbury CM. Multiplanar CT and MRI of collections in the retropharyngeal space: is it an abscess? AJR. 2011;196:426‐434. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

