Langerhans cell histiocytosis: A rare cause of pathological rib fracture
- PMID: 33768993
- PMCID: PMC7970081
- DOI: 10.5606/tgkdc.dergisi.2021.19685
Langerhans cell histiocytosis: A rare cause of pathological rib fracture
Abstract
Langerhans cell histiocytosis, formerly known as histiocytosis X, represents clonal proliferations of the antigen-presenting dendritic cells, which are normally found in many organs. It is a rare disease which tends to affect children and adolescents. In particular, adult-onset type is very rare. Herein, we present a female adult diagnosed with Langerhans cell histiocytosis of the rib without any systemic involvement which was successfully treated with surgery.
Keywords: Bone lesion; Langerhans cell histiocytosis; chest pain.
Copyright © 2021, Turkish Society of Cardiovascular Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declared no conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
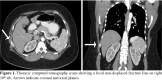

References
-
- Tombak A, Tiftik EN. Langerhans Hücreli Histiositozis. Turkiye Klinikleri J Hematol-Special Topics. 2013;6:74–79.
-
- Baumgartner I, von Hochstetter A, Baumert B, Luetolf U, Follath F. Langerhans"-cell histiocytosis in adults. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1997;28:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Howarth DM, Gilchrist GS, Mullan BP, Wiseman GA, Edmonson JH, Schomberg PJ. Langerhans cell histiocytosis: diagnosis, natural history, management, and outcome. Cancer. 1999;85:2278–2290. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
