Analysis of the SARS-CoV-2-host protein interaction network reveals new biology and drug candidates: focus on the spike surface glycoprotein and RNA polymerase
- PMID: 33769912
- PMCID: PMC8040492
- DOI: 10.1080/17460441.2021.1909566
Analysis of the SARS-CoV-2-host protein interaction network reveals new biology and drug candidates: focus on the spike surface glycoprotein and RNA polymerase
Abstract
Introduction: The COVID-19 pandemic originated from the emergence of anovel coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, which has been intensively studied since its discovery in order to generate the knowledge necessary to accelerate the development of vaccines and antivirals. Of note, many researchers believe there is great potential in systematically identifying host interactors of viral factors already targeted by existing drugs.Areas Covered: Herein, the authors discuss in detail the only available large-scale systematic study of the SARS-CoV-2-host protein-protein interaction network. More specifically, the authors review the literature on two key SARS-CoV-2 drug targets, the Spike surface glycoprotein, and the RNA polymerase. The authors also provide the reader with their expert opinion and future perspectives.Expert opinion: Interactions made by viral proteins with host factors reveal key functions that are likely usurped by the virus and, as aconsequence, points to known drugs that can be repurposed to fight viral infection and collateral damages that can exacerbate various disease conditions in COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; SARS-CoV-2; SARS-CoV-2-host protein interactome; antiviral drugs discovery; spike protein.
Figures
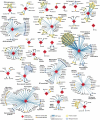
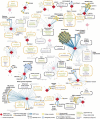


References
-
- Gates B. Responding to Covid-19 — a once-in-a-century pandemic? N Engl J Med. 2020;382(18):1677–1679. - PubMed
-
- Gordon DE, Jang GM, Bouhaddou M, et al. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature. 2020. July;583(7816):459–468. - PMC - PubMed
-
•• This paper provides the first extensive analysis of protein-protein interactions involving SARS-CoV2 proteins and host factors. The identification of host interactors allows to extract information about drugs that can be repurposed to eventually serve as a treatment for COVID–19
-
- Dunham WH, Mullin M, Gingras AC. Affinity-purification coupled to mass spectrometry: basic principles and strategies. Proteomics. 2012. May;12(10):1576–1590. - PubMed
-
- Cloutier P, Poitras C, Faubert D, et al. Upstream ORF-encoded ASDURF is a novel prefoldin-like subunit of the PAQosome. J Proteome Res. 2020. January 3;19(1):18–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
