COVID-19 in CXR: From Detection and Severity Scoring to Patient Disease Monitoring
- PMID: 33769939
- PMCID: PMC8545163
- DOI: 10.1109/JBHI.2021.3069169
COVID-19 in CXR: From Detection and Severity Scoring to Patient Disease Monitoring
Abstract
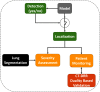
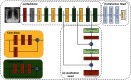
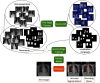
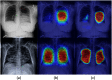
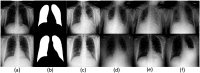
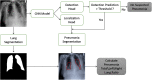
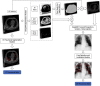
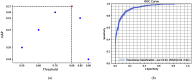
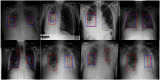
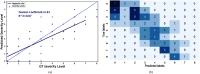
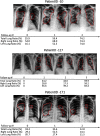
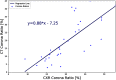
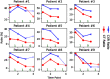
This work estimates the severity of pneumonia in COVID-19 patients and reports the findings of a longitudinal study of disease progression. It presents a deep learning model for simultaneous detection and localization of pneumonia in chest Xray (CXR) images, which is shown to generalize to COVID-19 pneumonia. The localization maps are utilized to calculate a "Pneumonia Ratio" which indicates disease severity. The assessment of disease severity serves to build a temporal disease extent profile for hospitalized patients. To validate the model's applicability to the patient monitoring task, we developed a validation strategy which involves a synthesis of Digital Reconstructed Radiographs (DRRs - synthetic Xray) from serial CT scans; we then compared the disease progression profiles that were generated from the DRRs to those that were generated from CT volumes.
Figures
References
-
- Jacobi A., Chung M., Bernheim A., and Eber C., “Portable chest x-ray in coronavirus disease-19 (covid-19): A pictorial review,” Clinical Imaging, vol. 64, pp. 35.42, 2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0899707120301017 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

