Neuropsychiatric symptoms in early stage of Alzheimer's and non-Alzheimer's dementia, and the risk of progression to severe dementia
- PMID: 33770167
- PMCID: PMC8437074
- DOI: 10.1093/ageing/afab044
Neuropsychiatric symptoms in early stage of Alzheimer's and non-Alzheimer's dementia, and the risk of progression to severe dementia
Abstract
Background: Neuropsychiatric symptoms (NPSs) in early dementia have been suggested to predict a higher risk of dementia progression. However, the literature is not yet clear whether the risk is similar across Alzheimer's dementia (AD) and non-Alzheimer's dementia (non-AD), as well as across different NPSs. This study examined the association between NPSs in early dementia and the risk of progression to severe dementia, specifically in AD and non-AD, as well as across various NPSs.
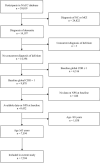
Method: This cohort study included 7,594 participants who were ≥65 years and had early dementia (global Clinical Dementia Rating [CDR] = 1). Participants completed Neuropsychiatric-Inventory-Questionnaire at baseline and were followed-up almost annually for progression to severe dementia (global CDR = 3) (median follow-up = 3.5 years; interquartile range = 2.1-5.9 years). Cox regression was used to examine progression risk, stratified by AD and non-AD.
Results: The presence of NPSs was associated with risk of progression to severe dementia, but primarily in AD (HR 1.4, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.1-1.6) and not in non-AD (HR 0.9, 95% CI: 0.5-1.5). When comparing across various NPSs, seven NPSs in AD were associated with disease progression, and they were depression, anxiety, apathy, delusions, hallucinations, irritability and motor disturbance (HR 1.2-1.6). In contrast, only hallucinations and delusions were associated with disease progression in non-AD (HR 1.7-1.9).
Conclusions: NPSs in early dementia-especially among individuals with AD-can be useful prognostic markers of disease progression. They may inform discussion on advanced care planning and prompt clinical review to incorporate evidence-based interventions that may address disease progression.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s dementia; advanced dementia; behavioural and psychological symptoms of dementia; dementia progression; non-Alzheimer’s dementia; older people.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Geriatrics Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Kales HC, Lyketsos CG, Miller EM, Ballard C. Management of behavioral and psychological symptoms in people with Alzheimer's disease: an international Delphi consensus. Int Psychogeriatr 2019; 31: 83–90. - PubMed
-
- Lopez OL, Schwam E, Cummings Jet al. Predicting cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease: an integrated analysis. Alzheimers Dement 2010; 6: 431–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P50 AG005142/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016573/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047266/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047366/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028383/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG033514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG053760/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG023501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG035982/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008051/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG049638/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG012300/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008017/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072977/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/GF/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

