Evaluation of sample pooling for SARS-CoV-2 RNA detection in nasopharyngeal swabs and salivas on the Roche Cobas 6800
- PMID: 33770658
- PMCID: PMC7944801
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104790
Evaluation of sample pooling for SARS-CoV-2 RNA detection in nasopharyngeal swabs and salivas on the Roche Cobas 6800
Abstract
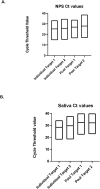
The Roche Cobas SARS-CoV-2 test recently received an Emergency Use Authorization from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration UA for pooling of up to six nasopharyngeal swab samples (NPS). We evaluated the 6-pool approach on both NPS and saliva samples using 564 samples (20 positive NPS and saliva samples each and 262 negative NPS and saliva samples each). The sensitivity of the Roche SARS-CoV-2 RNA test for pooled NPS samples was 100 % (95 %CI: 83.2-100 %) and the sensitivity for pooled saliva samples was 90 % (95 % CI: 68.3-98.8 %). Given the high throughput of the Roche Cobas 6800, pooling of 6 samples has the potential to significantly increase testing capacity without significant loss in sensitivity.
Keywords: RT-PCR EUA; SARS-CoV-2; Saliva; Sample pooling.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Sample Pooling for SARS-CoV-2 Detection in Nasopharyngeal Swab and Saliva Samples with the Idylla SARS-CoV-2 Test.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0099621. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00996-21. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34756076 Free PMC article.
-
Testing individual and pooled saliva samples for sars-cov-2 nucleic acid: a prospective study.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021 Nov;101(3):115478. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2021.115478. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34364098 Free PMC article.
-
Saliva is Comparable to Nasopharyngeal Swabs for Molecular Detection of SARS-CoV-2.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Sep 3;9(1):e0016221. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00162-21. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34406838 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR: Saliva or nasopharyngeal swab? Rapid review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 10;16(6):e0253007. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253007. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34111196 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR Using Different Sample Sources: Review of the Literature.Ear Nose Throat J. 2021 Apr;100(2_suppl):131S-138S. doi: 10.1177/0145561320953231. Epub 2020 Aug 31. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021. PMID: 32865458 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Sample Pooling for SARS-CoV-2 Detection in Nasopharyngeal Swab and Saliva Samples with the Idylla SARS-CoV-2 Test.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0099621. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00996-21. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34756076 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 saliva testing using RT-PCR: a systematic review.Int J Infect Dis. 2022 Aug;121:166-171. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2022.05.008. Epub 2022 May 13. Int J Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35577250 Free PMC article.
-
Update of Guidelines for Laboratory Diagnosis of COVID-19 in Korea.Ann Lab Med. 2022 Jul 1;42(4):391-397. doi: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.4.391. Ann Lab Med. 2022. PMID: 35177559 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for Scaling up SARS-CoV-2 Molecular Testing Capacity.Clin Lab Med. 2022 Jun;42(2):261-282. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2022.02.006. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Clin Lab Med. 2022. PMID: 35636826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taqman PACMAN: a simple molecular approach for positive rapid antigen test confirmation during periods of low prevalence.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 May 2;12(5):e0407323. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04073-23. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38567975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Holshue M.L., DeBolt C., Lindquist S., Lofy K.H., Wiesman J., Bruce H., Spitters C., Ericson K., Wilkerson S., Tural A., Diaz G., Cohn A., Fox L., Patel A., Gerber S.I., Kim L., Tong S., Lu X., Lindstrom S., Pallansch M.A., Weldon W.C., Biggs H.M., Uyeki T.M., Pillai S.K., Washington State -nCo VCIT First Case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382:929–936. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anonymous . The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); 2020. CDC COVID Data Tracker.
-
- Babady N.E., McMillen T., Jani K., Viale A., Robilotti E.V., Aslam A., Diver M., Sokoli D., Mason G., Shah M.K., Korenstein D., Kamboj M. Performance of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 real-time RT-PCR tests on oral rinses and saliva samples. J. Mol. Diagn. 2021;23(1):3–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2020.10.018. Jan. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barat B., Das S., De Giorgi V., Henderson D.K., Kopka S., Lau A.F., Miller T., Moriarty T., Palmore T.N., Sawney S., Spalding C., Tanjutco P., Wortmann G., Zelazny A.M., Frank K.M. Pooled saliva specimens for SARS-CoV-2 testing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020 doi: 10.1128/JCM.02486-20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous