Spontaneous Vocal Fold Polyps Remission after Lockdown for Covid-19 Pandemic: Does Vocal Load Matter?
- PMID: 33771429
- PMCID: PMC7959267
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2021.03.006
Spontaneous Vocal Fold Polyps Remission after Lockdown for Covid-19 Pandemic: Does Vocal Load Matter?
Abstract
Objective: During the Italian lockdown for Covid-19 emergency, due to stay-at-home orders, many people experienced an unusual period of voice rest. The present case series aims at reporting the spontaneous regression of some vocal fold polyps during the Italian lockdown for SARS-CoV2 pandemic.
Methods: Five patients with voice complaints presenting to a tertiary referral center and diagnosed with vocal fold polyps before the lockdown were included. Because of the lockdown restrictive measures, planned elective surgical procedures were suspended. The patients were re-assessed immediately after lockdown. Multidimensional voice assessments were conducted before and after the lockdown period through laryngostroboscopies, perceptual voice evaluations, electroacoustic analysis and self assessments.
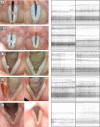
Results: The patients included in the present case series experienced a complete or nearly complete remission of symptoms. Videolaryngostroboscopies documented a complete or nearly complete regression of the polyps. Voices considerably improved both perceptually and electroacoustically. Self assessments showed a reduction of voice-related complaints.
Conclusions: The present study suggests that daily vocal load reduction may play a critical role in the conservative management of vocal fold polyps.
Keywords: Covid-19; Lockdown; Remission; SARS-CoV2; Vocal fold polyps; Vocal load.
Copyright © 2021 The Voice Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Salute.gov.it [Internet]. Italia: Ministero della salute; c2020 [cited 2020 Oct 02]. Covid-19 - Situazione in Italia. Available from: http://www.salute.gov.it/portale/nuovocoronavirus.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

