The Burkholderia pseudomallei intracellular 'TRANSITome'
- PMID: 33772012
- PMCID: PMC7998038
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22169-1
The Burkholderia pseudomallei intracellular 'TRANSITome'
Abstract
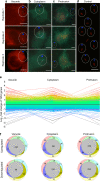
Prokaryotic cell transcriptomics has been limited to mixed or sub-population dynamics and individual cells within heterogeneous populations, which has hampered further understanding of spatiotemporal and stage-specific processes of prokaryotic cells within complex environments. Here we develop a 'TRANSITomic' approach to profile transcriptomes of single Burkholderia pseudomallei cells as they transit through host cell infection at defined stages, yielding pathophysiological insights. We find that B. pseudomallei transits through host cells during infection in three observable stages: vacuole entry; cytoplasmic escape and replication; and membrane protrusion, promoting cell-to-cell spread. The B. pseudomallei 'TRANSITome' reveals dynamic gene-expression flux during transit in host cells and identifies genes that are required for pathogenesis. We find several hypothetical proteins and assign them to virulence mechanisms, including attachment, cytoskeletal modulation, and autophagy evasion. The B. pseudomallei 'TRANSITome' provides prokaryotic single-cell transcriptomics information enabling high-resolution understanding of host-pathogen interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Burkholderia pseudomallei BopE suppresses the Rab32-dependent defense pathway to promote its intracellular replication and virulence.mSphere. 2024 Nov 21;9(11):e0045324. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00453-24. Epub 2024 Oct 21. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 39431830 Free PMC article.
-
In silico prediction of host-pathogen protein interactions in melioidosis pathogen Burkholderia pseudomallei and human reveals novel virulence factors and their targets.Brief Bioinform. 2021 May 20;22(3):bbz162. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbz162. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 32444871
-
A DUF4148 family protein produced inside RAW264.7 cells is a critical Burkholderia pseudomallei virulence factor.Virulence. 2020 Dec;11(1):1041-1058. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1806675. Virulence. 2020. PMID: 32835600 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular insights into Burkholderia pseudomallei and Burkholderia mallei pathogenesis.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2010;64:495-517. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.112408.134030. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20528691 Review.
-
Intracellular replication of the well-armed pathogen Burkholderia pseudomallei.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016 Feb;29:94-103. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2015.11.007. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26803404 Review.
Cited by
-
Burkholderia pseudomallei and melioidosis.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2024 Mar;22(3):155-169. doi: 10.1038/s41579-023-00972-5. Epub 2023 Oct 4. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 37794173 Review.
-
Burkholderia pseudomallei BopE suppresses the Rab32-dependent defense pathway to promote its intracellular replication and virulence.mSphere. 2024 Nov 21;9(11):e0045324. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00453-24. Epub 2024 Oct 21. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 39431830 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial esterases reverse lipopolysaccharide ubiquitylation to block host immunity.Cell Host Microbe. 2024 Jun 12;32(6):913-924.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2024.04.012. Cell Host Microbe. 2024. PMID: 38870903 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D (1α,25(OH)2D3) supplementation minimized multinucleated giant cells formation and inflammatory response during Burkholderia pseudomallei infection in human lung epithelial cells.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 9;18(2):e0280944. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280944. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36758060 Free PMC article.
-
A virulence activator of a surface attachment protein in Burkholderia pseudomallei acts as a global regulator of other membrane-associated virulence factors.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jan 16;13:1063287. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1063287. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36726566 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

