Cost-effectiveness of Triple Therapy vs. Biologic Treatment Sequence as First-line Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients after Methotrexate Failure
- PMID: 33772743
- PMCID: PMC8217385
- DOI: 10.1007/s40744-021-00300-4
Cost-effectiveness of Triple Therapy vs. Biologic Treatment Sequence as First-line Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients after Methotrexate Failure
Abstract
Introduction: A clinical trial (RACAT) reported the noninferiority of triple therapy compared to biologic agents (etanercept + methotrexate), and previous studies confirmed that biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) are more expensive but less beneficial than triple therapy for patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in whom methotrexate (MTX) fails. However, from the perspective of the Chinese healthcare system, the cost-effectiveness of triple therapy versus bDMARD treatment sequences as a first-line therapy for patients with RA is still unclear.
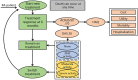
Methods: An individual patient simulation model was used to extrapolate the lifetime cost and health outcomes by tracing patients from initial treatment through switches to further treatment lines in a sequence. Therapeutic efficacy and physical function were evaluated using the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) response, 28-Joint Disease Activity Score (DAS28), and Health Assessment Questionnaire score. All input parameters in the model were derived from published studies, national databases, local hospitals, and experts' opinions. Both direct costs and indirect costs were taken into consideration. Probabilistic and one-way sensitivity analyses were performed to test the uncertainty of the model, as were multiple scenario analyses.
Results: The lifetime analysis demonstrated that triple therapy was associated with lower costs and quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) than bDMARD sequences. These resulted in incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) ranging from $87,090/QALY to $104,032/QALY, higher than the willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold in China ($30,950/QALY). The baseline DAS28 impacted the model outcomes the most. Scenario analyses indicated that adding triple therapy to bDMARD sequences as a first-, second-, third-, or fourth-line therapy is very cost-effective, at a WTP of $10,316/QALY.
Conclusions: From a Chinese payer perspective, triple therapy as first-line treatment in treatment sequence could be regarded as cost-effectiveness option for patients who failed MTX, compared to bDMARDs as first-line treatment, and instead of prescribing triple therapy as a substitute for bDMARDs as a first-line treatment, adding triple therapy to the bDMARD treatment sequence is likely to be very cost-effective for patients with active RA compared to bDMARD sequences.
Keywords: Biologic treatment sequence; Cost-effectiveness analysis; Rheumatoid arthritis; Triple therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tofacitinib for Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis After the Failure of Disease-Modifying Anti-rheumatic Drugs: An Evidence Review Group Perspective of a NICE Single Technology Appraisal.Pharmacoeconomics. 2018 Sep;36(9):1063-1072. doi: 10.1007/s40273-018-0639-0. Pharmacoeconomics. 2018. PMID: 29546668 Review.
-
Triple Therapy Versus Biologic Therapy for Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis.Ann Intern Med. 2017 Jul 4;167(1):8-16. doi: 10.7326/M16-0713. Epub 2017 May 30. Ann Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28554192
-
Sequences of biological treatments for patients with moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis in the era of treat-to-target in China: a cost-effectiveness analysis.Clin Rheumatol. 2022 Jan;41(1):63-73. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05876-4. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Clin Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 34373933
-
Cost-Effectiveness of Baricitinib for Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis After Methotrexate Failed in China.Rheumatol Ther. 2021 Jun;8(2):863-876. doi: 10.1007/s40744-021-00308-w. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Rheumatol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33893943 Free PMC article.
-
Sarilumab for Previously-Treated Moderate or Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Evidence Review Group Perspective of a NICE Single Technology Appraisal.Pharmacoeconomics. 2018 Dec;36(12):1427-1437. doi: 10.1007/s40273-018-0677-7. Pharmacoeconomics. 2018. PMID: 29882210 Review.
Cited by
-
Cost-effectiveness of janus kinase inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cost-utility studies.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 13;13:1090361. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1090361. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36582538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou Y-S, An Y, Li C, Xiao-ying Z, Duan T, Zhu J, Li X, Wang L. A multicenter study of deformity and disability in rheumatoid arthritis patients in China. Chin J Rheumatol. 2013;17(8):526–532. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-7480.2013.08.006. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

