Neutralizing and protective human monoclonal antibodies recognizing the N-terminal domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
- PMID: 33773105
- PMCID: PMC7962591
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.029
Neutralizing and protective human monoclonal antibodies recognizing the N-terminal domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
Abstract
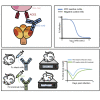
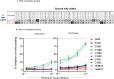
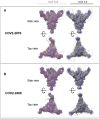
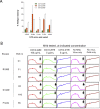
Most human monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 recognize the spike (S) protein receptor-binding domain and block virus interactions with the cellular receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. We describe a panel of human mAbs binding to diverse epitopes on the N-terminal domain (NTD) of S protein from SARS-CoV-2 convalescent donors and found a minority of these possessed neutralizing activity. Two mAbs (COV2-2676 and COV2-2489) inhibited infection of authentic SARS-CoV-2 and recombinant VSV/SARS-CoV-2 viruses. We mapped their binding epitopes by alanine-scanning mutagenesis and selection of functional SARS-CoV-2 S neutralization escape variants. Mechanistic studies showed that these antibodies neutralize in part by inhibiting a post-attachment step in the infection cycle. COV2-2676 and COV2-2489 offered protection either as prophylaxis or therapy, and Fc effector functions were required for optimal protection. Thus, natural infection induces a subset of potent NTD-specific mAbs that leverage neutralizing and Fc-mediated activities to protect against SARS-CoV-2 infection using multiple functional attributes.
Keywords: N-terminal domain; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus; monoclonal antibodies; neutralizing antibodies; viral antibodies.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests M.E.F., E.D., and B.J.D. are employees of Integral Molecular. B.J.D. is a shareholder of Integral Molecular. M.S.D. is a consultant for Inbios, Vir Biotechnology, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, and Carnival Corporation and is on the Scientific Advisory Boards of Moderna and Immunome, and the Diamond laboratory at Washington University School of Medicine has received sponsored research agreements from Emergent BioSolutions, Moderna, and Vir Biotechnology. J.E.C. has served as a consultant for Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, and Luna Biologics, is a member of the Scientific Advisory Boards of CompuVax and Meissa Vaccines, and is founder of IDBiologics. The Crowe laboratory at Vanderbilt University Medical Center has received unrelated sponsored research agreements from IDBiologics and AstraZeneca.
Figures







Update of
-
Neutralizing and protective human monoclonal antibodies recognizing the N-terminal domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Jan 20:2021.01.19.427324. doi: 10.1101/2021.01.19.427324. bioRxiv. 2021. Update in: Cell. 2021 Apr 29;184(9):2316-2331.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.029. PMID: 33501445 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Comment in
-
An NTD supersite of attack.Cell Host Microbe. 2021 May 12;29(5):744-746. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2021.04.010. Cell Host Microbe. 2021. PMID: 33984277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnes C.O., West A.P., Jr., Huey-Tubman K.E., Hoffmann M.A.G., Sharaf N.G., Hoffman P.R., Koranda N., Gristick H.B., Gaebler C., Muecksch F., et al. Structures of human antibodies bound to SARS-CoV-2 spike reveal common epitopes and recurrent features of antibodies. Cell. 2020;182:828–842.e16. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

