Dexmedetomidine ameliorates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in vivo and in vitro by preserving mitochondrial dynamic equilibrium through the HIF-1a/HO-1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 33774474
- PMCID: PMC8027777
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101954
Dexmedetomidine ameliorates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in vivo and in vitro by preserving mitochondrial dynamic equilibrium through the HIF-1a/HO-1 signaling pathway
Abstract
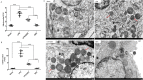
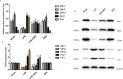
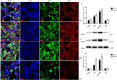
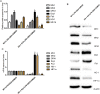
Increasing lines of evidence identified that dexmedetomidine (DEX) exerted protective effects against sepsis-stimulated acute lung injury via anti-inflammation, anti-oxidation and anti-apoptosis. However, the mechanisms remain unclear. Herein, we investigated whether DEX afforded lung protection by regulating the process of mitochondrial dynamics through the HIF-1a/HO-1 pathway in vivo and in vitro. Using C57BL/6J mice exposed to lipopolysaccharide, it was initially observed that preemptive administration of DEX (50μg/kg) alleviated lung pathologic injury, reduced oxidative stress indices (OSI), improved mitochondrial dysfunction, upregulated the expression of HIF-1α and HO-1, accompanied by shifting the dynamic course of mitochondria into fusion. Moreover, HO-1-knockout mice or HO-1 siRNA transfected NR8383 cells were pretreated with HIF-1α stabilizer DMOG and DEX to validate the effect of HIF-1a/HO-1 pathway on DEX-mediated mitochondrial dynamics in a model of endotoxin-induced lung injury. We found that pretreatment with DEX and DMOG distinctly relieved lung injury, decreased the levels of mitochondrial ROS and mtDNA, reduced OSI, increased nuclear accumulation of HIF-1a and HO-1 protein in wild type mice but not HO-1 KO mice. Similar observations were recapitulated in NC siRNA transfected NR8383 cells after LPS stimulation but not HO-1 siRNA transfected cells. Concertedly, DEX reversed the impaired mitochondrial morphology in LPS stimulated-wild type mice or NC siRNA transfected NR8383 cells, upregulated the expression of mitochondrial fusion protein, while downregulated the expression of fission protein in HIF-1a/HO-1 dependent pathway. Altogether, our data both in vivo and in vitro certified that DEX treatment ameliorated endotoxin-induced acute lung injury by preserving the dynamic equilibrium of mitochondrial fusion/fission through the regulation of HIF-1a/HO-1 signaling pathway.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Dexmedetomidine; Endotoxin; Heme oxygenase-1; Hypoxia-inducible factor 1; Mitochondrial dynamics.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Cecconi M., Evans L., Levy M., Rhodes A. Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet. 2018;392:75–87. - PubMed
-
- Lelubre C., Vincent J.L. Mechanisms and treatment of organ failure in sepsis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018;14:417–427. - PubMed
-
- Yu J., Shi J., Wang D., Dong S., Zhang Y., Wang M. Heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide- regulated mitochondrial dynamic equilibrium contributes to the attenuation of endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in rats and in lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages. Anesthesiology. 2016;125:1190–1201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

