Hypermetabolic lymphadenopathy following administration of BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine: incidence assessed by [18F]FDG PET-CT and relevance to study interpretation
- PMID: 33774684
- PMCID: PMC8003894
- DOI: 10.1007/s00259-021-05314-2
Hypermetabolic lymphadenopathy following administration of BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine: incidence assessed by [18F]FDG PET-CT and relevance to study interpretation
Abstract
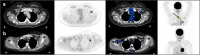
Purpose: Nationwide mass vaccination against Covid-19 started in Israel in late 2020. Soon we identified on [18F]FDG PET-CT studies vaccine-associated hypermetabolic lymphadenopathy (VAHL) in axillary or supraclavicular lymph nodes (ASLN) ipsilateral to the vaccination site. Sometimes, differentiation between the malignant and benign nature of the hypermetabolic lymphadenopathy (HLN) could not be made, and equivocal HLN (EqHL) was reported. The purpose of the study was to determine the overall incidence of VAHL after BNT162b2 vaccination and also its relevance to PET-CT interpretation in oncologic patients.
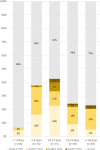
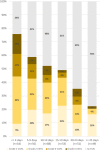
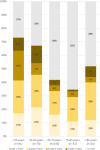
Methods: A total of 951 consecutive patients that underwent [18F]FDG PET-CT studies in our department were interviewed regarding the sites and dates of the vaccine doses. A total of 728 vaccinated patients (All-Vac group) were included: 346 received the first dose only (Vac-1 group) and 382 received the booster dose as well (Vac-2 group). Studies were categorized as no HLN, malignant-HLN (MHL), VAHL, or EqHL. In studies with VAHL, location, [18F]FDG-intensity uptake and nodes size were recorded.
Results: The incidences of HLN were 45.6%, 36.4%, and 53.9% in All-Vac, Vac-1, and Vac-2 groups, respectively. VAHL was reported in 80.1% of vaccinated patients with HLN. Lower incidences of VAHL were found during the first 5 days or in the third week after the first vaccine and beyond 20 days after the booster dose. In 49 of 332 (14.8%) vaccinated patients, we could not determine whether HLN was MHL or VAHL. Breast cancer and lymphoma were the leading diseases with EqHL.
Conclusion: VAHL is frequently observed after BNT162b2 administration, more commonly and with higher intensity following the booster dose. To minimize false and equivocal reports in oncological patients, timing of [18F]FDG PET-CT should be based on the time intervals found to have a lower incidence of VAHL, and choice of vaccine injection site should be advised, mainly in patients where ASLN are a relevant site of tumor involvement.
Keywords: Axillary lymph nodes; Covid-19; False-positive [18F]FDG uptake; Oncologic imaging; Vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Medical imaging in times of pandemic: focus on the cornerstones of successful imaging.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021 Jun;48(6):1724-1725. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05331-1. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33770202 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Prevalence of Increased FDG PET/CT Axillary Lymph Node Uptake Beyond 6 Weeks after mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination.Radiology. 2021 Sep;300(3):E345-E347. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021210886. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Radiology. 2021. PMID: 33904778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coates EE, Costner PJ, Nason MC, Herrin DM, Conant S, Herscovitch P, Sarwar UN, Holman L, Mitchell J, Yamshchikov G, Koup RA. Lymph node activation by PET/CT following vaccination with licensed vaccines for human papillomaviruses. Clin Nucl Med. 2017;42(5):329–334. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000001603. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

