Echinococcus granulosus cyst fluid suppresses inflammatory responses by inhibiting TRAF6 signalling in macrophages
- PMID: 33775265
- PMCID: PMC11010193
- DOI: 10.1017/S0031182021000548
Echinococcus granulosus cyst fluid suppresses inflammatory responses by inhibiting TRAF6 signalling in macrophages
Abstract
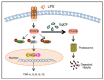
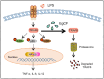
Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato has complex defence mechanisms that protect it from the anti-parasitic immune response for long periods. Echinococcus granulosus cyst fluid (EgCF) is involved in the immune escape. Nevertheless, whether and how EgCF modulates the inflammatory response in macrophages remains poorly understood. Here, real-time polymerase chain reaction and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay revealed that EgCF could markedly attenuate the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced production of pro-inflammatory factors including tumour necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-6 but increase the expression of IL-10 at mRNA and protein levels in mouse peritoneal macrophages and RAW 264.7 cells. Mechanically, western blotting and immunofluorescence assay showed that EgCF abolished the activation of nuclear factor (NF)-κB p65, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and ERK1/2 signalling pathways by LPS stimulation in mouse macrophages. EgCF's anti-inflammatory role was at least partly contributed by promoting proteasomal degradation of the critical adaptor TRAF6. Moreover, the EgCF-promoted anti-inflammatory response and TRAF6 proteasomal degradation were conserved in human THP-1 macrophages. These findings collectively reveal a novel mechanism by which EgCF suppresses inflammatory responses by inhibiting TRAF6 and the downstream activation of NF-κB and MAPK signalling in both human and mouse macrophages, providing new insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying the E. granulosus-induced immune evasion.
Keywords: Cystic echinococcosis; EgCF; TRAF6; inflammation; macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

