Addition of Astatine-211-Labeled Anti-CD45 Antibody to TBI as Conditioning for DLA-Identical Marrow Transplantation: A Novel Strategy to Overcome Graft Rejection in a Canine Presensitization Model: "Radioimmunotherapy to Overcome Transfusion-Induced Sensitization"
- PMID: 33775618
- PMCID: PMC8217096
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtct.2021.02.018
Addition of Astatine-211-Labeled Anti-CD45 Antibody to TBI as Conditioning for DLA-Identical Marrow Transplantation: A Novel Strategy to Overcome Graft Rejection in a Canine Presensitization Model: "Radioimmunotherapy to Overcome Transfusion-Induced Sensitization"
Abstract
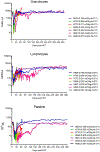
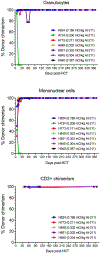
In a canine model of presensitization using donor blood transfusions, 100% of historical control dogs receiving 9.2 Gy total body irradiation (TBI) conditioning before dog leukocyte antigen (DLA)-identical marrow grafts had graft rejection. In this presensitization model, we investigated whether the addition of monoclonal antibody (mAb)-based targeted radioimmunotherapy (RIT) with astatine-211 (211At) to TBI could overcome graft rejection. 211At is an alpha-particle-emitting isotope that has a short path length, very high energy, and a short t½ of 7.2 hours, which allowed targeting radiation to the T cells responsible for graft rejection. Normal canine recipients were given three preceding transfusions of unirradiated whole blood on days -24, -17, and -10 before transplant from their DLA-identical marrow donors. 211At-anti-CD45 mAb was administered on day -3, and TBI followed by marrow grafts on day 0. Six of the 7 dogs (86%) achieved sustained engraftment as assessed by 100% donor chimerism in mononuclear cells, granulocytes, and CD3+ T cells. One dog receiving the lowest CD34+ cell content (0.35 × 106 cells/kg) rejected the graft. There were no late rejections in dogs followed up to 1 year. Graft-versus-host disease was seen in one dog. 211At-anti-CD45 mAb in combination with TBI as conditioning was successful in abrogating graft rejection in 86% of dogs in this presensitization model. 211At-anti-CD45 mAb conditioning with TBI may serve as a novel promising strategy to overcome graft rejection in heavily transfused patients with red cell disorders.
Keywords: Astatine-211; DLA-identical marrow transplantation; Graft rejection; Transfusion sensitized.
Copyright © 2021 The American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in relation to the work.
Figures

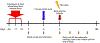
Similar articles
-
CD154 blockade and donor-specific transfusions in DLA-identical marrow transplantation in dogs conditioned with 1-Gy total body irradiation.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007 Feb;13(2):164-71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2006.10.031. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007. PMID: 17241922 Free PMC article.
-
The use of an anti-TCRalphabeta monoclonal antibody to control host-versus-graft reactions in canine marrow allograft recipients conditioned with low dose total body irradiation.Transplantation. 1999 May 27;67(10):1329-35. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199905270-00007. Transplantation. 1999. PMID: 10360586
-
Durable donor engraftment after radioimmunotherapy using α-emitter astatine-211-labeled anti-CD45 antibody for conditioning in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation.Blood. 2012 Feb 2;119(5):1130-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-09-380436. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22134165 Free PMC article.
-
Protective conditioning against GVHD and graft rejection after combined organ and hematopoietic cell transplantation.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2008 Jan-Feb;40(1):48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2007.06.019. Epub 2007 Sep 10. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2008. PMID: 17827036 Review.
-
Outpatient allografting in hematologic malignancies and nonmalignant disorders--applying lessons learned in the canine model to humans.Cancer Treat Res. 2002;110:149-75. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0919-6_8. Cancer Treat Res. 2002. PMID: 11908197 Review.
Cited by
-
Astatine-211 radiolabelling chemistry: from basics to advanced biological applications.EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2024 Oct 4;9(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s41181-024-00298-4. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2024. PMID: 39365487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astatine-211 based radionuclide therapy: Current clinical trial landscape.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 6;9:1076210. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1076210. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36687417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astatine-211 and actinium-225: two promising nuclides in targeted alpha therapy.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Nov 25;57(3):327-343. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024206. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 39587859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiopharmaceuticals for Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy: New Targets, New Therapies-Alpha-Emitters, Novel Targets.Cancer J. 2024 May-Jun 01;30(3):218-223. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000720. Cancer J. 2024. PMID: 38753757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody based conditioning for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 20;13:1031334. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1031334. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36341432 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Storb R, Epstein RB, Rudolph RH, Thomas ED. The effect of prior transfusion on marrow grafts between histocompatible canine siblings. J Immunol. 1970;105:627–633. - PubMed
-
- Storb R, Rudolph RH, Graham TC, Thomas ED. The influence of transfusions from unrelated donors upon marrow grafts between histocompatible canine siblings. J Immunol. 1971;107:409–413. - PubMed
-
- Storb R, Weiden PL, Deeg HJ, et al. Rejection of marrow from DLA-identical canine littermates given transfusions before grafting: antigens involved are expressed on leukocytes and skin epithelial cells but not on platelets and red blood cells. Blood. 1979;54:477–484. - PubMed
-
- Bean MA, Storb R, Graham T, et al. Prevention of transfusion-induced sensitization to minor histocompatibility antigens on DLA-identical canine marrow grafts by gamma irradiation of marrow donor blood. Transplantation. 1991;52:956–960. - PubMed
-
- Bean MA, Graham T, Appelbaum FR, et al. Gamma-irradiation of pretransplant blood transfusions from unrelated donors prevents sensitization to minor histocompatibility antigens on dog leukocyte antigen-identical canine marrow grafts. Transplantation. 1994;57:423–426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

