Environmental survival of SARS-CoV-2 - A solid waste perspective
- PMID: 33775678
- PMCID: PMC7997151
- DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111015
Environmental survival of SARS-CoV-2 - A solid waste perspective
Abstract
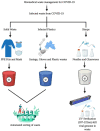
The advent of COVID-19 has kept the whole world on their toes. Countries are maximizing their efforts to combat the virus and to minimize the infection. Since infectious microorganisms may be transmitted by variety of routes, respiratory and facial protection is required for those that are usually transmitted via droplets/aerosols. Therefore this pandemic has caused a sudden increase in the demand for personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, masks, and many other important items since, the evidence of individual-to-individual transmission (through respiratory droplets/coughing) and secondary infection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). But the disposal of these personal protective measures remains a huge question mark towards the environmental impact. Huge waste generation demands proper segregation according to waste types, collection, and recycling to minimize the risk of infection spread through aerosols and attempts to implement measures to monitor infections. Hence, this review focuses on the impact of environment due to improper disposal of these personal protective measures and to investigate the safe disposal methods for these protective measures by using the safe, secure and innovative biological methods such as the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Ultraviolet (UV) lights for killing such deadly viruses.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Biomedical waste; Biomedical waste management; COVID-19; Environmental damage; Personnel protective equipment (PPE).
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Acharya D.B. The Book of Hospital Waste Management. 2000;1:92–96.
-
- Ali M.L., Alam M., Rahaman M.A.N.R. 7th International Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering. IEEE; 2012. RFID based e-monitoring system for municipal solid waste management; pp. 474–477. - DOI
-
- Anh Khoa T., Phuc C.H., Lam P.D., Nhu L.M.B., Trong N.M., Phuong N.T.H. Waste management system using IoT-based machine learning in university. Wireless Commun. Mobile Comput. 2020 doi: 10.1155/2020/6138637. - DOI
-
- Anila V., Ganesan H., Raja S.S.S., Govindasamy V., Arunachalam M., Narayanasamy A., Sivaprakash P., Rahman P.K., Gopalakrishnan A.V., Siama Z., Vellingiri B. Novel wastewater surveillance strategy for early detection of COVID–19 hotspots. Curr Opin Environ Sci Health. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.coesh.2020.05.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

