Cytokine Release Syndrome Induced by Immune-checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy for Non-small-cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 33775995
- PMCID: PMC8627810
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.5922-20
Cytokine Release Syndrome Induced by Immune-checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy for Non-small-cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
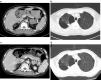
Immune-related adverse events, including autoimmune toxicity, may develop as a consequence of immune-checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) cancer therapy. Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is a severe and life-threatening cytokine-associated toxicity that can develop after adoptive T-cell therapy. We herein report a rare case of severe CRS after ICI therapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. He presented with a prolonged high fever, cardiogenic shock, and disseminated intravascular coagulation after the first course of programed death ligand-1 inhibitor and platinum-based doublet chemotherapy. He recovered by steroid pulse therapy and tocilizumab. CRS is a rare but life-threatening adverse event of ICI therapy and therefore warrants awareness.
Keywords: cytokine release syndrome; immune-checkpoint therapy; tocilizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Postow MA, Sidlow R, Hellmann MD. Immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade. N Engl J Med 378: 158-168, 2018. - PubMed
-
- Socinski MA, Jotte RM, Cappuzzo F, et al. Atezolizumab for first-line treatment of metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC. N Engl J Med 378: 2288-2301, 2018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical