The Pathological Role of Pro(Renin) Receptor in Renal Inflammation
- PMID: 33776491
- PMCID: PMC7989955
- DOI: 10.2147/JEP.S297682
The Pathological Role of Pro(Renin) Receptor in Renal Inflammation
Abstract
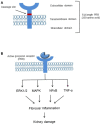
(Pro)renin receptor (PRR) is the recently discovered component of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAS). Many organs contain their own RAS, wherein PRR can exert organ-specific localized effects. The Binding of prorenin/renin to PRR activates angiotensin-dependent and independent pathways which leads to the development of physiological and pathological effects. Continued progress in PRR research suggests that the upregulation of PRR contributes to the development of hypertension, glomerular injury, and progression of kidney disease and inflammation. In the current review, we highlight the function of the PRR in renal inflammation in pathophysiological conditions.
Keywords: diabetes; hypertension; prorenin receptor; renal inflammation; renin-angiotensin system.
© 2021 Quadri et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources