Determinant Factors of Neonatal Near Miss Among Neonates in Gurage Zone Hospitals, Ethiopia: A Case-Control Study
- PMID: 33776508
- PMCID: PMC7989378
- DOI: 10.2147/PHMT.S302363
Determinant Factors of Neonatal Near Miss Among Neonates in Gurage Zone Hospitals, Ethiopia: A Case-Control Study
Abstract
Introduction: It is highly economical and commendable to identify the determinants of neonatal near miss which will be utilized as proxy determinants of neonatal mortality rate. However, neither determinants of neonatal mortality rate nor a determinant of a neonatal near miss are adequately investigated specifically within the study area. Therefore, this study is aimed to identify the determinants of neonatal near-miss among neonates admitted in hospitals of the Gurage zone, Southern Ethiopia.
Methods and materials: Unmatched case-control study was conducted to identify factors associated with neonatal near-miss among neonates admitted in Gurage zone hospitals. A pre-tested structured interviewer-administered questionnaire was used to collect the data. Besides, data related to the clinical diagnosis of neonates and managements given were extracted from patient records. In this study, a total of 105 cases and 209 controls have participated. To recruit cases and controls consecutive sampling methods and simple random sampling techniques were used respectively. Data were entered using Epi Data software and exported to SPPS for analysis. To identify the determinate factors of the outcome variable binary and multivariable logistic regression were employed.
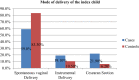
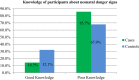
Results: The determinate factors of the outcome variable include a history of abortion with AOR 3.9 [95%C1 3.53-10.15], referred from other health care institution AOR 7.53[95% CI 3.99-14.22], severe maternal morbidity during pregnancy AOR 4.57[95% CI 1.77-11.79], cesarean section mode of delivery 4.45[95% CI 1.76-11.25], and good essential newborn care knowledge AOR 3.33[95% CI 1.54-7.19].
Conclusion: In this study, easily modifiable/preventable maternal and health service utilization-related factors are increasing the menace of a neonatal near-miss in the Gurage zone. It is the signal that shows the primary health care program needs to be further enhanced to bring more desirable health outcomes and/or effectiveness of health policies needs to be examined to introduce more impactful strategies.
Keywords: Ethiopia; determinants; neonatal near miss; severe neonatal morbidity.
© 2021 Abebe et al.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no competing interests declared by the authors.
Figures

References
-
- Ezbakhe F, Pérez-foguet A. Child mortality levels and trends. Demographic Res. 2020;43:1263–1296. doi: 10.1007/s00270-020-02514-5 - DOI
-
- World Health Organization. Survive and thrive: transforming care for every small and sick newborn. Key findings. 2018. Available from: https://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/documents/care-small-sick-....
-
- Every woman every child: the global strategy for women’s, children’s, and adolescents’ health (2016–2030). 2015. Available from: http://www.who.int/pmnch/media/events/2015/gs_2016_30.pdf. Accessed March11, 2021.
-
- UNICEF, World Health Organization. Every newborn progress report 2018 executive summary – healthy newborn network. Available from: https://www.healthynewbornnetwork.org/resource/every-newborn-progress-re....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

