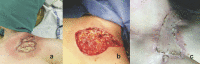
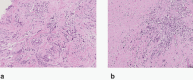
Postsurgical Pyoderma Gangrenosum in a Breast Cancer Patient: A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 33776698
- PMCID: PMC7983549
- DOI: 10.1159/000509745
Postsurgical Pyoderma Gangrenosum in a Breast Cancer Patient: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
Pyoderma gangrenosum is a rare skin necrotizing disease that can arise on a site of surgical trauma. Its pathogenesis has recently been related to dysregulation of the immune system, with inflammatory bowel disease representing the most commonly underlying systemic conditions. Several authors have also reported an association with solid malignancies (especially gastrointestinal and breast cancer). We describe the case of a 39-year-old patient diagnosed with a locally advanced, triple-negative breast cancer who developed a pyoderma gangrenosum on the surgical wound after a CVC implant with systemic complications. As the diagnosis and management of postsurgical pyoderma gangrenosum can be challenging for clinicians, underlying conditions as autoimmune disease and solid tumors have to be considered in order to guide treatment.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Pathergy; Pyoderma gangrenosum; Solid tumors.
Copyright © 2021 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ruocco E, Sangiuliano S, Gravina AG, Miranda A, Nicoletti G. Pyoderma gangrenosum: an updated review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009;23((9)):1008–17. - PubMed
-
- Ahronowitz I, Harp J, Shinkai K. Etiology and management of pyoderma gangrenosum: a comprehensive review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2012;13((3)):191–211. - PubMed
-
- Pereira N, Brites MM, Gonçalo M, Tellechea O, Figueiredo A. Pyoderma gangrenosum -- a review of 24 cases observed over 10 years. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52((8)):938–45. - PubMed
-
- Shahi V, Wetter DA. Pyoderma gangrenosum associated with solid organ malignancies. Int J Dermatol. 2015;54((9)):e351–7. - PubMed
-
- Patel DK, Locke M, Jarrett P. Pyoderma gangrenosum with pathergy: a potentially significant complication following breast reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2017;70((7)):884–92. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials