Expression of Dopamine D1-4 and Serotonin 5-HT1A-3A Receptors in Blood Mononuclear Cells in Schizophrenia
- PMID: 33776821
- PMCID: PMC7988204
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.645081
Expression of Dopamine D1-4 and Serotonin 5-HT1A-3A Receptors in Blood Mononuclear Cells in Schizophrenia
Abstract
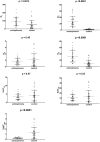
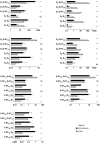
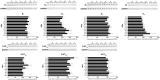
Introduction: The aim of this study was to determine the mRNA expression profile of dopamine D1, D2, D3, D4 and serotonin 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A, and 5-HT3A receptors in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in schizophrenia and the in vitro effect of antipsychotics on the expression of these receptors in PBMCs of healthy subjects. Materials and Methods: Twenty-seven patients with schizophrenia and 29 healthy controls were recruited for the study. All study subjects underwent thorough clinical assessment, including anthropometric and body composition measurements. The expression of mRNA for dopamine D1-4 and serotonin 5-HT1A-3A receptors was measured using quantitative RT-PCR in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. In vitro mRNA and protein expression of these receptors was measured using quantitative RT-PCR and Western Blotting in PBMCs cultured with quetiapine, haloperidol, aripiprazole, risperidone, olanzapine or clozapine at IC50, half of IC50, and one-quarter of IC50 concentrations. Results: The key finding was that the schizophrenia group demonstrated significantly higher mRNA expression of D1, D2 and D4 receptors (p < 0.001), and significantly lower mRNA expression of 5-HT3A receptors (p < 0.01). After adjusting for smoking, the mRNA expression of D1 lost its significance, while that of D3, 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A became significant (all three were lower in the schizophrenia group). These receptors also demonstrated different ratios of mRNA expression in the schizophrenia group. The in vitro experiments showed that high concentrations of antipsychotics influenced the mRNA and protein expression of all studied receptors. Conclusion: Schizophrenia patients display a distinctive pattern of dopamine and serotonin receptor mRNA expression in blood mononuclear cells. This expression is little affected by antipsychotic treatment and it may therefore serve as a useful diagnostic biomarker for schizophrenia.
Keywords: PBMCs; Schizophrenia; biomarkers; dopamine receptors; serotonin receptors.
Copyright © 2021 Wysokiński, Kozłowska, Szczepocka, Łucka, Agier, Brzezińska-Błaszczyk and Sobierajska.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Risperidone Decreases Expression of Serotonin Receptor-2A (5-HT2A) and Serotonin Transporter (SERT) but Not Dopamine Receptors and Dopamine Transporter (DAT) in PBMCs from Patients with Schizophrenia.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 28;17(2):167. doi: 10.3390/ph17020167. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399382 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin receptors: their key role in drugs to treat schizophrenia.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2003 Oct;27(7):1159-72. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2003.09.010. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2003. PMID: 14642974 Review.
-
Risperidone compared with new and reference antipsychotic drugs: in vitro and in vivo receptor binding.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1996 Mar;124(1-2):57-73. doi: 10.1007/BF02245606. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1996. PMID: 8935801
-
Equivalent occupancy of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors with clozapine: differentiation from other atypical antipsychotics.Am J Psychiatry. 2004 Sep;161(9):1620-5. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.161.9.1620. Am J Psychiatry. 2004. PMID: 15337652
-
Aripiprazole: a review of its use in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.Drugs. 2004;64(15):1715-36. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200464150-00010. Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15257633 Review.
Cited by
-
An In Vitro Study for the Role of Schizophrenia-Related Potential miRNAs in the Regulation of COMT Gene.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Oct;61(10):7680-7690. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04070-2. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38427212 Free PMC article.
-
Antipsychotic-induced bone loss: the role of dopamine, serotonin and adrenergic receptor signalling.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 May 25;11:1184550. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1184550. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37305679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Captive ERVWE1 triggers impairment of 5-HT neuronal plasticity in the first-episode schizophrenia by post-transcriptional activation of HTR1B in ALKBH5-m6A dependent epigenetic mechanisms.Cell Biosci. 2023 Nov 21;13(1):213. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01167-4. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37990254 Free PMC article.
-
Risperidone Decreases Expression of Serotonin Receptor-2A (5-HT2A) and Serotonin Transporter (SERT) but Not Dopamine Receptors and Dopamine Transporter (DAT) in PBMCs from Patients with Schizophrenia.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 28;17(2):167. doi: 10.3390/ph17020167. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399382 Free PMC article.
-
The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Psychiatric Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 24;23(19):11245. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911245. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232548 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

