Compromised Dynamic Cerebral Autoregulation in Patients With Central Disorders of Hypersomnolence
- PMID: 33776891
- PMCID: PMC7991911
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.634660
Compromised Dynamic Cerebral Autoregulation in Patients With Central Disorders of Hypersomnolence
Abstract
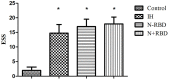
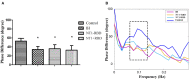
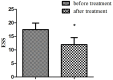
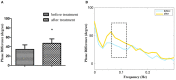
Objective: We aimed to investigate the dynamic cerebral autoregulation (dCA) in patients with central disorders of hypersomnolence during wakefulness. Methods: Thirty-six patients with central disorders of hypersomnolence were divided into three groups according to polysomnography and multiple sleep latency test results: the idiopathic hypersomnia group (IH), narcolepsy type 1 without rapid-eye-movement sleep behavior disorder group (NT1-RBD), and narcolepsy type 1 with rapid-eye-movement sleep behavior disorder group (NT1 + RBD), with 12 patients in each group. Twelve sex- and age-matched healthy controls were recruited. We assessed the Epworth sleepiness scale (ESS) and dCA of all subjects. dCA was assessed by analyzing the phase difference (PD) using transfer function analysis. The ESS and dCA were analyzed before and after standardized treatment in 24 patients with narcolepsy type 1. Results: The overall PD of the IH, NT1-RBD, and NT1 + RBD groups were lower than that of the control group (P < 0.001). There were no significant differences between the overall PD of the NT1-RBD and NT1 + RBD group (P > 0.05). The ESS scores decreased and the overall PD increased after treatment in 24 patients with narcolepsy type 1 (P < 0.001). Multivariable analysis showed that mean sleep latency in multiple sleep latency test was independently associated with impaired overall PD (P < 0.05). Conclusions: The dCA is impaired in patients with central disorders of hypersomnolence. The impairment of dCA occurs irrespective of NT1-RBD/+RBD. The ESS score and dCA improved in patients with narcolepsy type 1 after medication treatment. The mean sleep latency in multiple sleep latency test was independently associated with impaired dCA. Clinical Trial Registration: www.ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier: NCT02752139.
Keywords: central disorders of hypersomnolence; dynamic cerebral autoregulation; idiopathic hypersomnia; narcolepsy type 1; rapid-eye-movement sleep behavior disorder.
Copyright © 2021 Deng, Zhang, Zhang, Tang, Guo, Lv, Wang and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Claassen JA, Meel-van den Abeelen AS, Simpson DM, Panerai RB. International Cerebral Autoregulation Research Network (CARNet). Transfer function analysis of dynamic cerebral autoregulation: a white paper from the International Cerebral Autoregulation Research Network. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (2016) 36:665–80. 10.1177/0271678X15626425 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

